Effort Estimation in Project Management: 7 Proven Techniques
- What is Effort Estimation in Project Management?
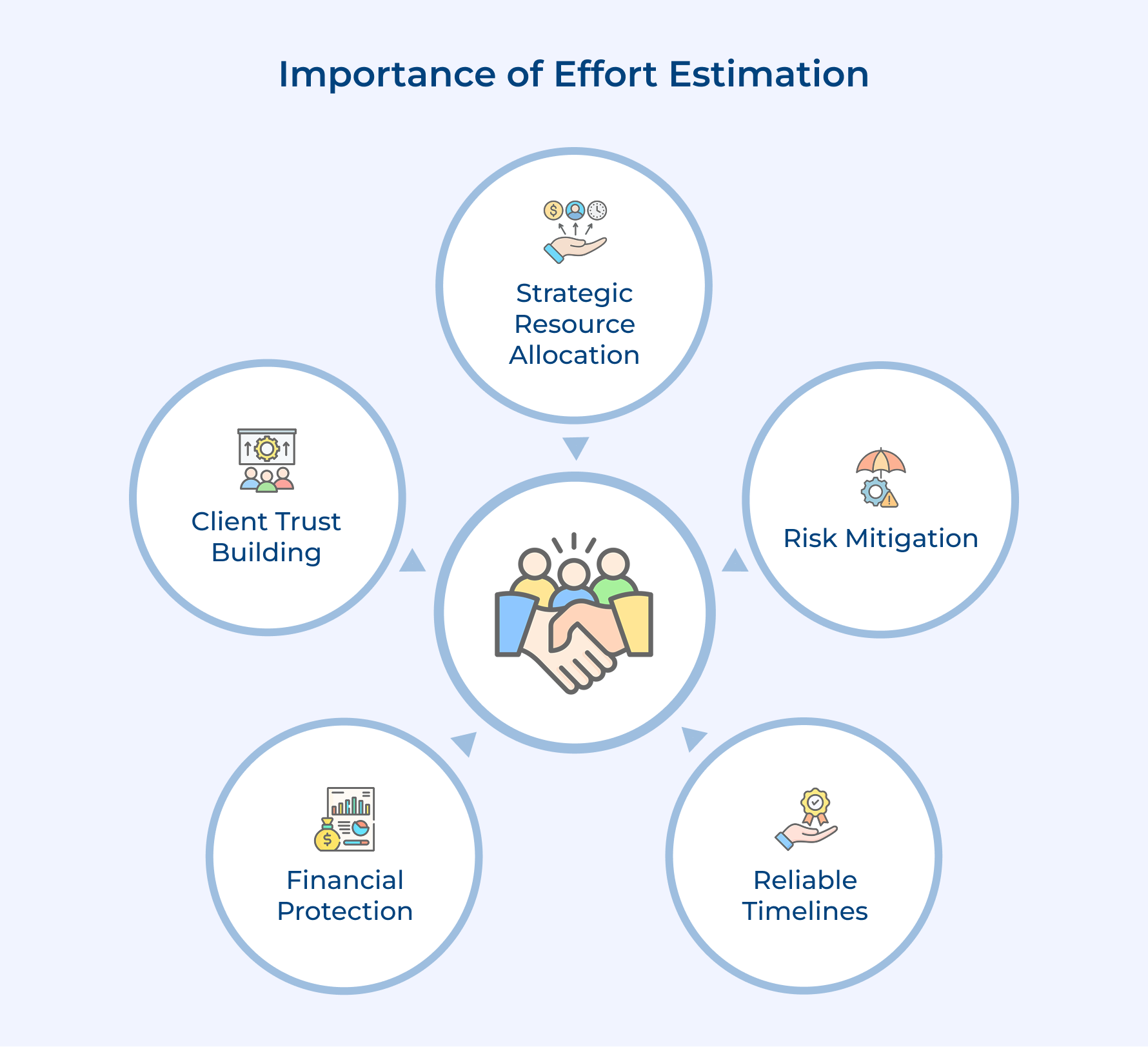
- Why is Effort Estimation Important?
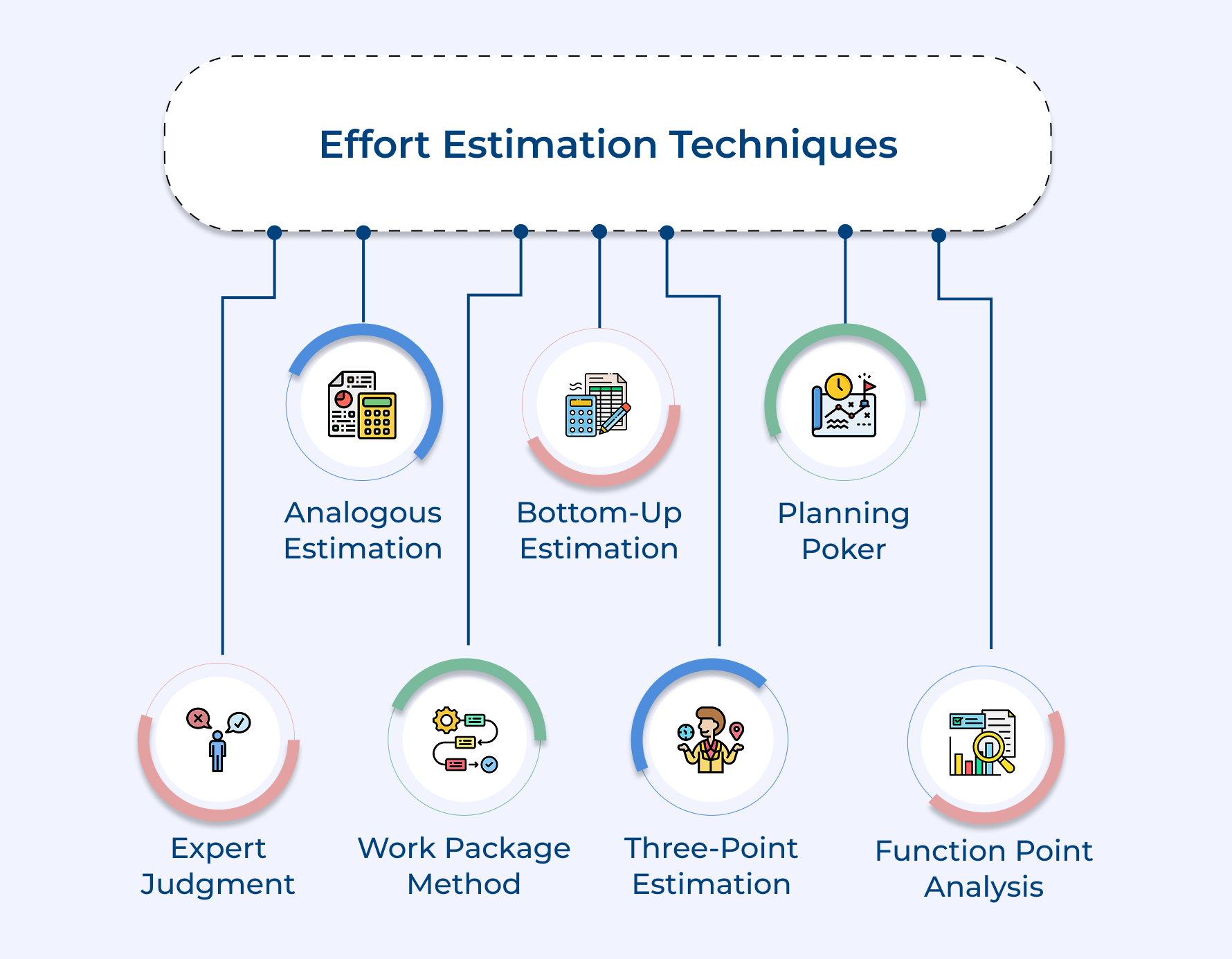
- 7 Essential Effort Estimation Techniques for Project Success
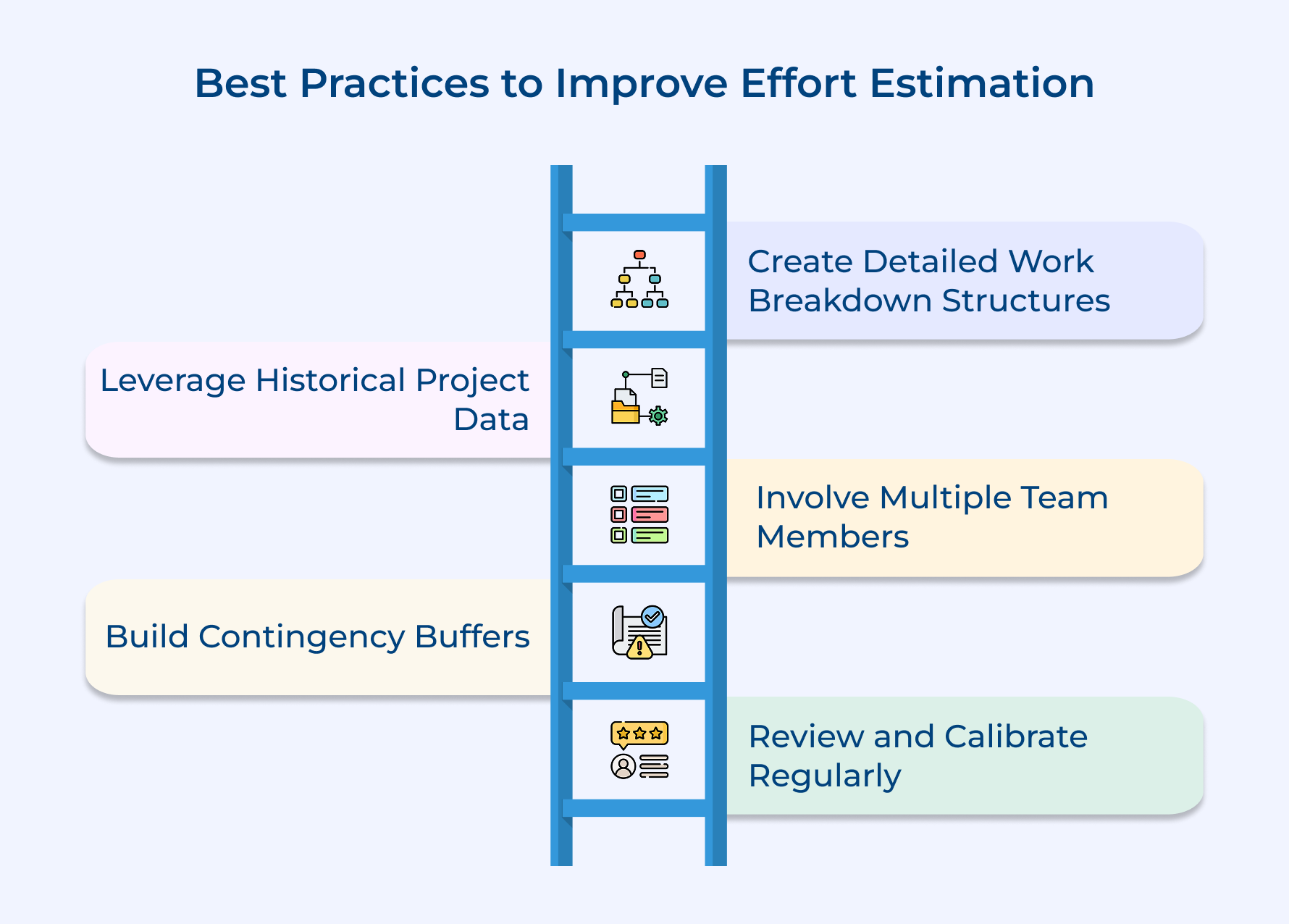
- Best Practices to Improve Effort Estimation in Project Management
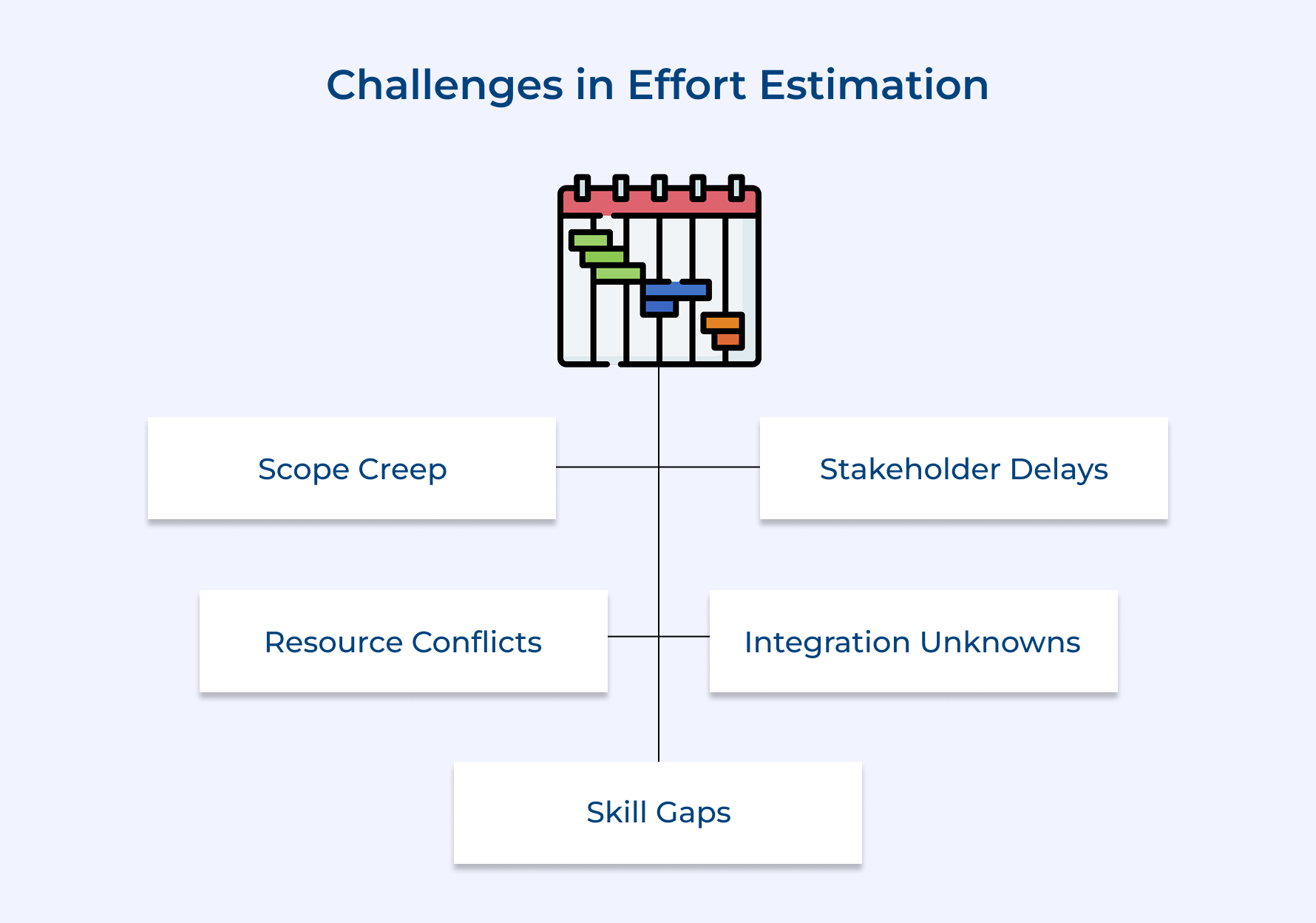
- Challenges and Pitfalls in Effort Estimation for Complex Projects
- Effort Estimation: Predicting Project Success with Precision
- FAQs about Effort Estimation

Key Highlights:
- Accurate effort estimation prevents budget overruns and missed deadlines in complex projects.
- Proven effort estimation techniques include expert judgment, top-down, bottom-up and Agile methods.
- Effort estimation in project management builds client trust and enables strategic resource allocation.
Most professional services projects miss deadlines and go over budget. This usually happens because teams underestimate the effort needed for complex deliverables. The result is unhappy clients and reduced profitability.
Poor estimation sets off a harmful cycle. Rushed teams cut corners on quality. Budget overruns eat into margins. Clients lose trust due to missed timelines, which damages long-term relationships.
Accurate effort estimation changes this. It turns planning from guesswork into a reliable process. Proven techniques help teams deliver consistent value. This leads to sustainable profits and stronger client partnerships.
What is Effort Estimation in Project Management?
Effort estimation is the process of predicting how much time and resources your team will need to complete specific project tasks or deliverables. It involves breaking down complex work into manageable pieces and calculating the human hours required for each component.
Poor effort estimation creates a domino effect that ripples through entire organizations and client relationships. When estimates are off-target, teams either rush through work compromising quality or exceed budgets creating financial strain. Accurate estimation builds trust with clients and enables realistic project timelines that protect both team wellbeing along with business sustainability.
Main purposes of effort estimation:
- Resource planning: Determine exactly how many people with specific skills you need for each project phase.
- Budget control: Calculate project costs accurately to maintain healthy profit margins and avoid financial surprises.
- Timeline management: Set realistic deadlines that account for actual work complexity rather than wishful thinking.
- Risk mitigation: Identify potential bottlenecks and resource conflicts before they derail project delivery.
- Client expectation setting: Provide transparent communication about project scope and delivery timelines from the start.
Why is Effort Estimation Important?
Effort estimation serves as the foundation that determines whether professional service firms thrive or struggle in competitive markets. Let’s look at some numbers:
- Only 46% of companies place a high priority on a culture that values project management.
- 75% of project managers say they have been asked to do too much work with too few resources.
These aspects define the importance of having effort estimation. Here are other reasons why you should consider it:
1. Financial Protection and Profitability Control
Accurate effort estimation acts like a financial shield that protects your firm from unexpected cost overruns and scope creep. When you predict resource needs correctly you can price projects appropriately while maintaining healthy profit margins throughout the engagement lifecycle.
2. Enhanced Client Trust and Relationship Management
Reliable estimation builds credibility with clients by demonstrating professional competence and transparency in project planning. This foundation of trust leads to stronger long-term relationships, repeat business as well as positive referrals that fuel sustainable growth.
3. Strategic Resource Allocation and Team Optimization
Proper effort estimation enables you to allocate your best talent to the right projects at optimal times. The strategic approach prevents resource conflicts, maximizes billable utilization rates as well as ensures team members work on projects that match their expertise levels.
4. Risk Mitigation and Contingency Planning
Through careful estimation you can identify potential bottlenecks, delivery risks and dependencies before they become project-threatening issues. This foresight allows teams to develop contingency plans and adjust timelines proactively rather than reactively managing crises.
5. Improved Project Timeline Management
When effort estimates are grounded in reality your project timelines become reliable commitments rather than wishful thinking. Predictability helps clients plan their own business activities around your deliverables while reducing stress for your internal teams.
7 Essential Effort Estimation Techniques for Project Success
Let’s explore seven essential effort estimation techniques that can help you navigate and forecast your project’s demands accurately.
1. Expert Judgment Estimation
Expert judgment is one of the most reliable effort estimation methods in professional services, especially when navigating complex, customized projects. Here’s how it works in real-world settings:
- Experience-based predictions: Senior consultants draw from years of hands-on experience to offer realistic time and effort estimates. They understand client behavior, hidden risks and delivery challenges.
- Cross-functional validation: Department heads from delivery, design and client success collaborate to refine estimates. This collective approach balances different perspectives and minimizes bias.
- Historical trend analysis: Teams review similar past projects to spot effort patterns and resource needs. This ensures estimates are grounded in real delivery data.
Expert judgment turns deep institutional knowledge into smarter project planning while building internal confidence and client trust.
2. Analogous Estimation Technique (Top-Down Approach)
Analogous estimation compares current projects with historically similar engagements to derive effort predictions through proven delivery patterns and established benchmarks. Similar past project comparison analysis serves as the foundation for top-down estimation by identifying projects with comparable scope complexity and client requirements.
Key comparison components:
- Project scope similarity
- client industry alignment
- delivery methodology consistency.
Here are some effort estimation examples that show how industry benchmark data improves accuracy through external validation.
- Healthcare consulting projects: Average 12-16 weeks for digital transformation initiatives across mid-market organizations.
- Financial services compliance: Standard 8-12 consultant months for regulatory framework implementation projects.
- Technology integration consulting: Typical 6-9 month timeline for enterprise software deployment and change management.
- Marketing strategy development: Industry standard 4-6 weeks for comprehensive brand positioning and go-to-market planning.
3. Work Package Method
The work package effort estimation template helps break down large projects into smaller, manageable units. It allows for more accurate effort planning by focusing on individual deliverables and complexity levels. Here’s how it works:
- Deliverable-focused time allocation: Each deliverable is treated as a separate unit with its own timeline and resource needs. This helps project managers estimate effort based on the actual work involved and the skills required.
- Milestone-driven effort planning: Milestones act as checkpoints for tracking progress while adjusting estimates as needed. They keep the team aligned and make it easier to correct course if things shift.
- Client requirement complexity assessment: Analyzing how complex each requirement is (including stakeholder input or integration hurdles) helps teams allocate the right amount of effort from the start.
4. Bottom-Up Estimation
Bottom-up estimation builds project effort predictions from granular task analysis upward creating comprehensive resource requirements through detailed work breakdown and individual component assessment.
Key questions to consider before implementing bottom-up estimation:
- What level of task granularity provides optimal estimation accuracy without excessive planning overhead?
- Do we have subject matter experts available to estimate specialized technical components accurately?
- How will we manage estimation variance when aggregating hundreds of individual task predictions?
- What mechanisms will track actual effort against estimates to improve future bottom-up accuracy?
These questions help establish estimation boundaries and ensure your team has the necessary expertise as well as processes to make bottom-up estimation successful.
Once you’ve addressed these foundational questions, it is important to understand how you can implement bottom-up estimation? Do it by systematically breaking down project deliverables into measurable tasks and aggregating individual effort predictions into comprehensive project timelines.
5. Three-Point Estimation Techniques (PERT Method)
Three-point estimation is a smart and practical effort estimation method that helps teams deal with uncertainty in professional services projects. Instead of relying on a single guess, it uses three estimates (optimistic, pessimistic and most likely) to calculate a weighted average. This gives you a more balanced and realistic prediction.
- Optimistic estimate: This is the best-case scenario. Everything goes smoothly. Resources are fully available, stakeholders respond quickly and there are no tech or scope issues. It shows the minimum effort required and helps teams spot when a project is outperforming expectations.
- Pessimistic estimate: This covers the worst-case scenario. Think resource shortages, scope creep, system integration problems and delayed approvals. It prepares teams to build contingency plans and allocate buffer time along with resources.
- Most likely estimate: This reflects typical project conditions. It assumes common challenges, standard engagement levels and usual approval delays. This estimate forms the foundation for your project plan, balancing known risks and expected performance.
Teams get a clearer picture of what’s possible, what could go wrong and what’s most probable by combining these three views. Thus, making three-point estimation a powerful tool for accurate planning and smarter delivery.
6. Planning Poker (Agile Estimation)
Planning Poker brings teams together in structured estimation sessions where participants use story points to determine effort requirements through consensus-building collectively. It further ensures relative sizing methodologies that promote collaborative decision-making.
This collaborative technique works by having team members independently estimate tasks using standardized point scales. It then discusses differences until reaching a consensus agreement on final estimates through multiple rounds of deliberation.
Best Practices:
- Include diverse team perspectives from technical delivery and client-facing roles to ensure comprehensive estimation coverage.
- Limit estimation sessions to two hours maximum to maintain focus and prevent decision fatigue among participants.
7. Function Point Analysis
Function Point Analysis quantifies software functionality through standardized measurement units enabling consistent effort predictions across technology projects and development initiatives.
Why does standardized measurement matter for effort estimation? For example, think of effort estimation like measuring ingredients for a recipe – without consistent units you cannot predict cooking time accurately. Software functionality measurement standardization provides the same reliability by creating uniform metrics that translate directly into predictable development.
Beyond standardization this method requires complexity factor adjustment calculations to account for varying technical challenges and implementation requirements across different project environments. These calculations ensure that effort estimates reflect the true complexity of each unique software development initiative rather than applying generic measurements.
Key adjustment factors to consider:
- Technical complexity level
- Integration requirements scope
- Performance optimization needs
- Security implementation standards.
Function Point Analysis transforms subjective estimation into objective measurement providing professional services firms with reliable data-driven approaches for technology project planning.
Best Practices to Improve Effort Estimation in Project Management
These proven practices help professional services firms build estimation accuracy while reducing project risks and client dissatisfaction.
1. Create Detailed Work Breakdown Structures Before Estimation
Breaking complex projects into granular tasks reveals hidden work that often gets overlooked in high-level estimates.
Key questions to ask yourself:
- What specific deliverables must we create for each project phase?
- Which tasks require specialized skills or external dependencies?
- Where might scope creep typically emerge based on client behavior patterns?
Detailed work breakdown structures serve as your estimation foundation by ensuring nothing falls through the cracks. This systematic approach helps identify resource conflicts early while providing clear task ownership and accountability throughout the engagement lifecycle.
2. Leverage Historical Data from Similar Past Projects
Your previous projects contain valuable estimation intelligence that most firms never fully utilize for future planning. Creating a searchable database of past project metrics transforms institutional knowledge into actionable estimation tools.
Historical data analysis reveals patterns that improve future estimation accuracy while helping teams avoid repeating past mistakes. This evidence-based approach builds client confidence through transparent planning processes grounded in proven delivery experiences rather than optimistic projections.
Consider these essential data points when building your historical reference library.
- Document actual hours spent versus original estimates.
- Record client-specific factors that influenced timeline changes
- resource requirements during delivery.
3. Involve Multiple Team Members in Estimation Processes
Estimation accuracy improves dramatically when multiple perspectives contribute to the planning process rather than relying on single-person predictions. Cross-functional input identifies blind spots while building team ownership of project commitments and realistic delivery expectations.
Essential team roles for comprehensive estimation:
- Technical specialists who understand implementation complexities
- Client-facing professionals who recognize stakeholder management challenges
- Project managers who coordinate interdependent tasks and resource allocation
Collaborative estimation sessions produce more reliable results because different team members bring unique insights about potential challenges. This shared responsibility approach also ensures that estimates reflect real-world constraints rather than theoretical best-case scenarios.
4. Build Contingency Buffers Into Your Estimates
Professional services projects inevitably encounter unexpected challenges that require additional time and resources for successful completion. Smart estimation includes planned buffers that protect both project quality and team wellbeing when complications arise.
Transparent contingency communication builds client trust by demonstrating professional planning while setting realistic expectations about potential timeline adjustments. This proactive approach prevents last-minute scrambling when projects encounter typical professional services challenges like scope changes or stakeholder delays.
5. Regularly Review and Calibrate Estimation Accuracy
Continuous improvement requires systematic analysis of estimation performance compared to actual project outcomes and resource consumption. Monthly reviews help teams identify patterns while adjusting future estimates based on real delivery data.
Regular calibration sessions transform estimation from art into science by creating feedback loops that improve prediction accuracy. Teams that consistently review their estimation performance develop increasingly reliable planning capabilities while building strong client relationships through dependable delivery commitments.
Critical metrics for estimation calibration:
- variance between estimated and actual hours
- estimation blind spots
- timeline accuracy and resource requirements measurement
Challenges and Pitfalls in Effort Estimation for Complex Projects
Complex projects present unique estimation challenges that can derail even experienced professional services teams. Understanding these common pitfalls helps organizations develop more robust planning processes and realistic client expectations.
Common Challenges in Effort Estimation:
- Scope creep and evolving requirements: Many projects start with unclear needs that grow over time. Traditional estimates often miss this ongoing discovery process, leading to underestimation.
- Task interdependencies and resource conflicts: Delays in one workstream often affect others. When estimates are made in isolation, they miss the ripple effect caused by sequential dependencies.
- Stakeholder availability and delays: Getting approvals and decisions from busy stakeholders takes longer than expected. Ignoring this leads to unrealistic timelines.
- Technical integration unknowns: System integration often uncovers hidden issues mid-project. These surprises are hard to account for without in-depth discovery.
- Team skill gaps and learning curves: New technologies or methods may require upskilling or external help. Estimates must include training or onboarding time.
Solutions Using Estimation Best Practices:
- Phase-based estimation with checkpoints: Break projects into stages with regular reviews to refine predictions.
- Cross-functional planning teams: Involve delivery leads, tech experts and client managers for balanced input.
- Early technical discovery: Run integration checks before finalizing your timeline.
- Skill and training analysis: Use effort estimation formulas that factor in ramp-up time.
- Risk-adjusted buffers: Add contingency based on uncertainty and complexity levels.
Effort Estimation: Predicting Project Success with Precision
Effort estimation serves as the foundational skill that separates successful professional services firms from those struggling with cost overruns and client dissatisfaction. Without accurate predictions teams cannot deliver consistent value or maintain sustainable business operations.
Mastering estimation techniques enables agencies to maximize billable utilization while minimizing project risks and building stronger client relationships through reliable delivery commitments. This precision transforms estimation from guesswork into competitive advantage that drives long-term profitability as well as operational excellence.
Limit time — not creativity
Everything you need for customer support, marketing & sales.
Pooja Deshpande is a content contributor at Kooper, focused on creating insightful resources that help agencies and service providers scale efficiently. Passionate about SaaS trends, content strategy, and operational excellence, she delivers practical, easy-to-implement guidance for modern business leaders.