Guide To Project Initiation: Steps, Benefits & Best Practices
- What is Project Initiation?
- Components Included in a Project Initiation Document (PID)
- Benefits of Project Initiation Phase
- Project Initiation Process: 7 Steps
- Best Practices for Project Initiation Phase
- Challenges Faced During Project Initiation
- Project Initiation as Your Foundation for Success
- FAQs about Project Initiation

Key Highlights:
- Project initiation sets clear goals, scope and stakeholder alignment to ensure your project starts with focus as well as direction.
- Learn proven project initiation steps including business case creation, feasibility checks and securing stakeholder buy-in for success.
- Effective project initiation prevents scope creep, improves resource planning and boosts success rates across all project management phases.
Rushing into execution without proper project initiation is like throwing in the dark — you might move fast, but you’ll likely miss the target. Many organizations burn through budgets on initiatives with unclear goals, no real stakeholder agreement and unrealistic resource plans. Thus, resulting in scope creep, budget blowouts and teams working twice as hard for half the impact.
Misaligned expectations erode trust and client relationships take the hit. Project initiation changes that. It’s the phase where loose concepts become structured plans, boundaries are set and everyone understands their role.
Grounding your project in shared clarity from the start will give your team the direction and stability needed to deliver results without unnecessary chaos.
What is Project Initiation?
Project initiation is the foundational phase where organizations formally define a new project and authorize its existence. This critical stage involves identifying the business need or opportunity that the project will address. Teams establish the project’s basic framework including its purpose and high-level scope. The phase culminates in creating formal documentation that gives the project official approval to proceed.
Impact on Project-Based Agencies and Professional Services
In agencies and professional services firms, project initiation directly shapes client relationships as well as sets expectations for the entire engagement. A thorough initiation process helps prevent scope creep and ensures all stakeholders understand deliverables. When done well, this phase builds client confidence and establishes the foundation for successful project delivery as well as future business opportunities.
People involved in project initiation:
- Project sponsor: The executive who champions the project and provides high-level direction as well as funding approval.
- Project manager: The professional responsible for planning the initiation activities and coordinating between all stakeholders.
- Business analyst: The person who identifies business requirements and translates them into project objectives as well as scope.
- Key stakeholders: The individuals or clients who will be affected by the project outcomes and have input on requirements.
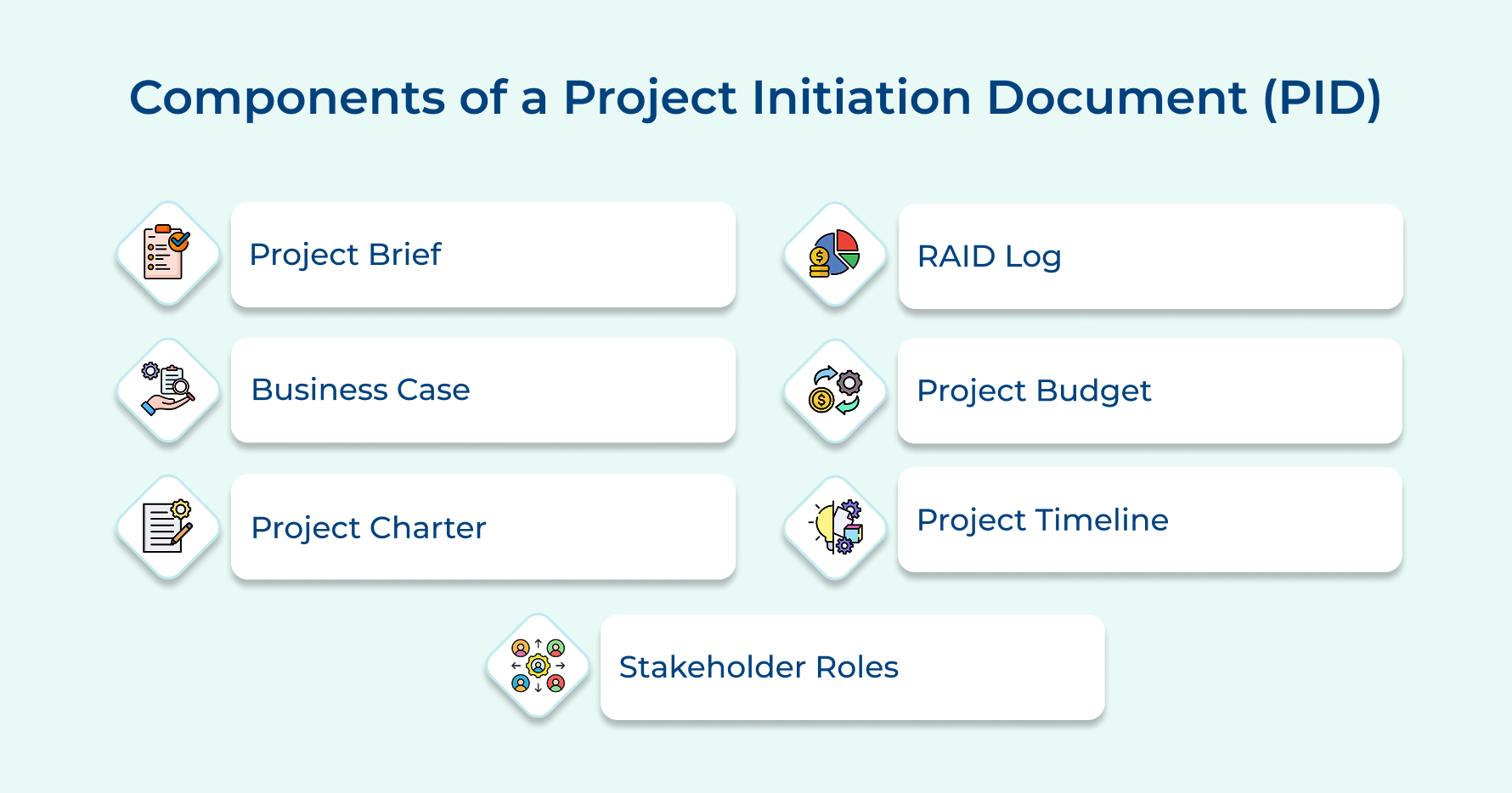
Components Included in a Project Initiation Document (PID)
A Project Initiation Document serves as the comprehensive blueprint that transforms project ideas into actionable plans. Understanding its components helps project managers create thorough documentation that guides successful project delivery.
Before diving into specific components, answering these fundamental questions helps establish proper context for your Project Initiation Document:
- What specific business problem does this project solve?
- Who has the authority to make final project decisions?
- What resources and budget are realistically available?
- How will we measure project success objectively?
These questions form the backbone of your PID because they force strategic thinking about your project’s purpose and constraints before detailed planning activities.
1. Project Brief
Consider the project brief as the “quick-read” version of your entire plan. It should be clear, simple and jargon-free. This is your elevator pitch to help any stakeholder instantly understand what the project is about without wading through technical details.
2. Business Case
This is where you prove the project’s worth. A solid business case shows how the investment pays off, aligns with strategic goals and supports smart resource management by weighing costs against expected benefits.
3. Project Charter
The charter is the green light. It formally grants authority, clarifies the project manager’s responsibilities and sets the tone for all planning, right through to project closure.
4. RAID Log
A RAID log tracks risks, assumptions, issues and dependencies so you’re not blindsided. It’s a practical tool for stakeholder analysis, ensuring potential challenges are visible and managed.
5. Project Budget
Here’s where you break down every anticipated cost like people, tools, vendors, etc. It’s your financial roadmap and a benchmark for monitoring as the project unfolds.
6. Project Timeline
The timeline maps out major phases, milestones and deadlines. Thus, helping stakeholders stay aligned and teams work in sync. It keeps delivery expectations crystal clear.
7. Stakeholder Roles
Stakeholder analysis isn’t just a kickoff task, it starts here. Clearly defining roles prevents confusion, speeds up decision-making and makes everyone’s contribution to success visible.
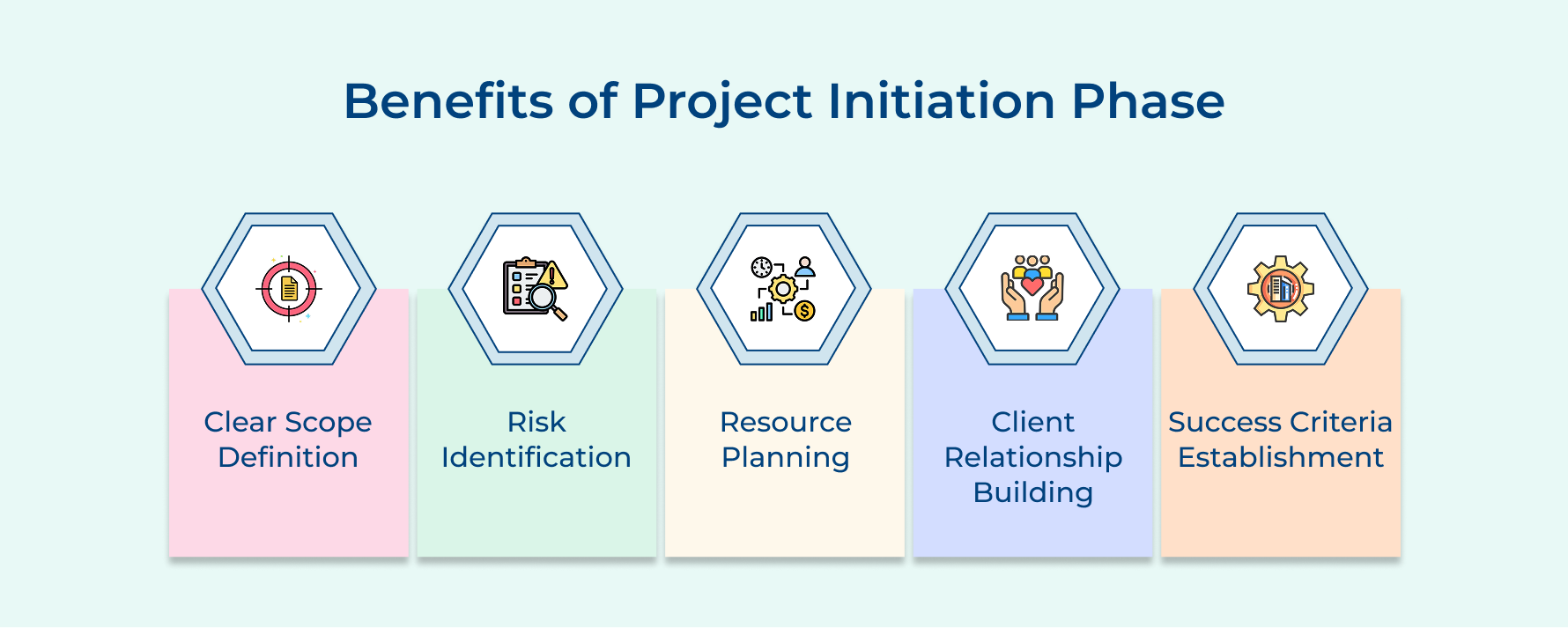
Benefits of Project Initiation Phase
The project initiation phase serves as the strategic foundation that determines if your project will thrive or struggle throughout its lifecycle. Here are the benefits to consider:
1. Clear Scope Definition and Boundary Setting
Project initiation establishes precise boundaries around what will and won’t be delivered. This clarity prevents scope creep that often derails agency projects and helps maintain profitability by keeping work within agreed parameters.
3. Risk Identification and Mitigation Planning
Early risk assessment during initiation helps agencies spot potential problems before they become costly issues. Teams can develop contingency plans and allocate resources appropriately, protecting both project timelines as well as client relationships.
4. Resource Planning and Budget Accuracy
Proper initiation allows agencies to estimate resource needs more accurately and create realistic budgets. This leads to better project margins and helps prevent the common problem of underestimating effort along with costs.
5. Client Relationship Foundation Building
The initiation phase establishes trust and credibility with clients through professional planning as well as clear communication. The strong foundation often leads to repeat business and referrals, which are crucial for agency growth.
6. Project Success Criteria Establishment
During initiation, teams define measurable success criteria that everyone agrees upon. Having these benchmarks established upfront makes it easier to demonstrate value to clients and measure project performance throughout the engagement.
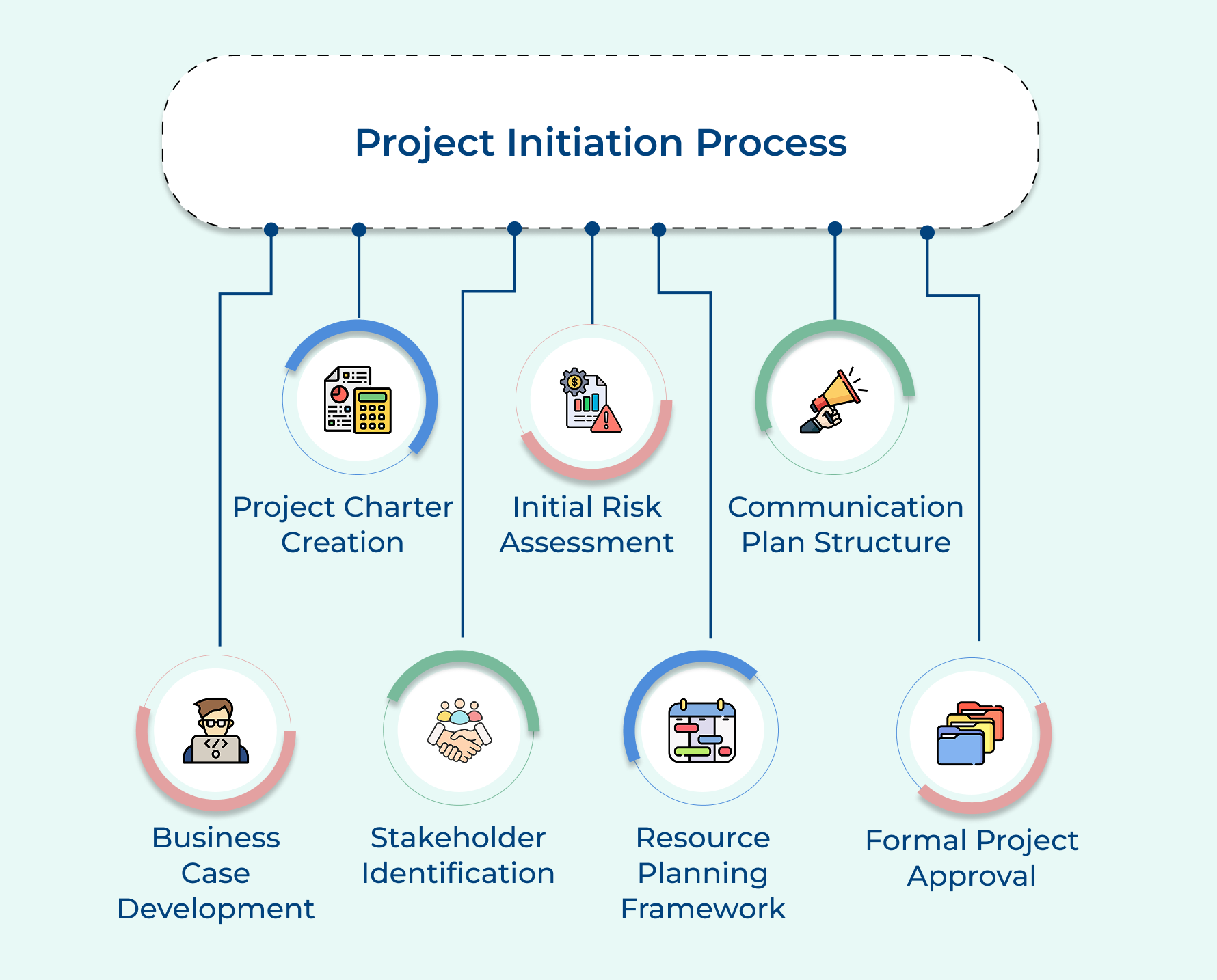
Project Initiation Process: 7 Steps
Let’s delve into these steps and uncover how each one plays a vital role in setting up your project for success.
1. Identify Business Need or Opportunity
Every strong project initiation starts with one question: Why are we doing this? Whether it’s solving a pressing problem or seizing a timely opportunity, the “why” sets your direction. To uncover it, ask:
- What specific problem are we solving?
- What opportunity is worth acting on now?
- How will this benefit our organization?
- What’s the risk if we do nothing?
Gather answers through stakeholder interviews, customer feedback, market research and your strategic plan. Sometimes the most valuable insights come from frontline employees who see challenges leadership hasn’t spotted. This step ensures you’re solving a real need, not chasing trends or personal preferences that drain resources.
2. Define Project Goals and Objectives
Once you know the “why,” you can define the “what.” This means turning broad needs into specific, measurable targets using SMART criteria:
- Specific – State exactly what you’ll achieve.
- Measurable – Decide how success will be tracked.
- Achievable – Keep goals realistic but challenging.
- Relevant – Align objectives with business strategy.
- Time-bound – Set deadlines to keep momentum.
Think of these as your project’s scorecard. For a website redesign, that could be improved conversion rates or higher user satisfaction. For a process improvement, it might be reduced errors or time savings. Clear goals help teams focus, measure success and keep stakeholders aligned.
3. Conduct Initial Feasibility Assessment
Before committing time and money, check if your idea can actually be delivered. This involves:
- Technical viability: Do you have the skills, tools and infrastructure? Can it integrate with current systems?
- Resource check: Do you have enough people, budget and time without overloading teams?
- Timeline and budget reality: Can you deliver within required deadlines as well as financial constraints and is it worth the opportunity cost?
Feasibility assessments prevent wasted effort on projects that can’t succeed under current conditions and they surface potential roadblocks early.
4. Identify Key Stakeholders and Sponsors
This component involves mapping everyone who influences or gets affected by your project outcomes. Stakeholder identification prevents surprises later and ensures you have the right people supporting your project from the beginning through completion.
When you struggle to identify your key stakeholders and sponsors during project initiation, these strategic questions provide clarity:
- Who has the authority to approve or cancel this project?
- Which departments or teams will be impacted by project outcomes?
- Who controls the budget and resources we need?
- Which external parties have influence over project success?
Here’s a practical approach that works better than just answering questions: create a simple stakeholder map on paper. Draw your project in the center and add circles around it representing different people or groups.
5. Develop High-Level Project Scope Statement
A project scope statement creates boundaries around what your project will and will not deliver. The definition prevents projects from growing beyond their original intent and helps teams stay focused on delivering specific outcomes.
The scope statement serves as your project’s contract with stakeholders. It documents major deliverables as well as sets clear expectations about what gets included in the project work and what stays outside the project boundaries.
Pro tips:
- Always write what you will NOT do as clearly as what you will do to prevent scope creep later.
- Keep your scope statement at a high level during initiation since detailed requirements come during the planning phase.
6. Create Project Charter Document
This step transforms your initiation work into a formal document that gives your project official existence. The charter serves as your project’s birth certificate and provides the foundation for future planning activities.
Keep charter language simple and focus on outcomes rather than detailed processes. Executives approving charters care more about business value than technical implementation details.
Project Charter Template Structure:
Project Title: [Clear descriptive name]
Project Sponsor: [Executive champion]
Business Need: [Why this project exists]
Project Objectives: [SMART goals]
High-Level Scope: [Major deliverables]
Initial Budget: [Financial requirements]
Timeline: [Start date and milestones]
Key Stakeholders: [Primary affected parties]
Authorization: [Signature lines]
A marketing agency creates a charter for a client’s website redesign. The charter specifies building a responsive website with improved user experience. It identifies the client’s marketing director as the primary stakeholder and establishes conversion rate improvements as success criteria.
7. Secure Formal Project Approval
This final step involves getting official authorization from decision-makers to proceed with your project. Formal approval provides a mandate and resources needed to move into detailed planning as well as execution.
Three proven methods help secure formal approval effectively:
- Executive presentation method: Schedule focused meetings with decision-makers to present your business case directly. Use visual aids and emphasize return on investment while allowing time for questions.
- Staged approval process: Break approval into smaller commitments starting with concept then budget approval. This reduces perceived risk and allows executives to maintain control over decisions.
- Stakeholder coalition building: Gather support from influential stakeholders before approaching final decision-makers. Multiple voices advocating creates momentum and demonstrates broader organizational support.
When presenting a customer relationship management system upgrade to executives, emphasize how the new system improves sales productivity by thirty percent. Include implementation costs alongside projected revenue increases to demonstrate clear business value.
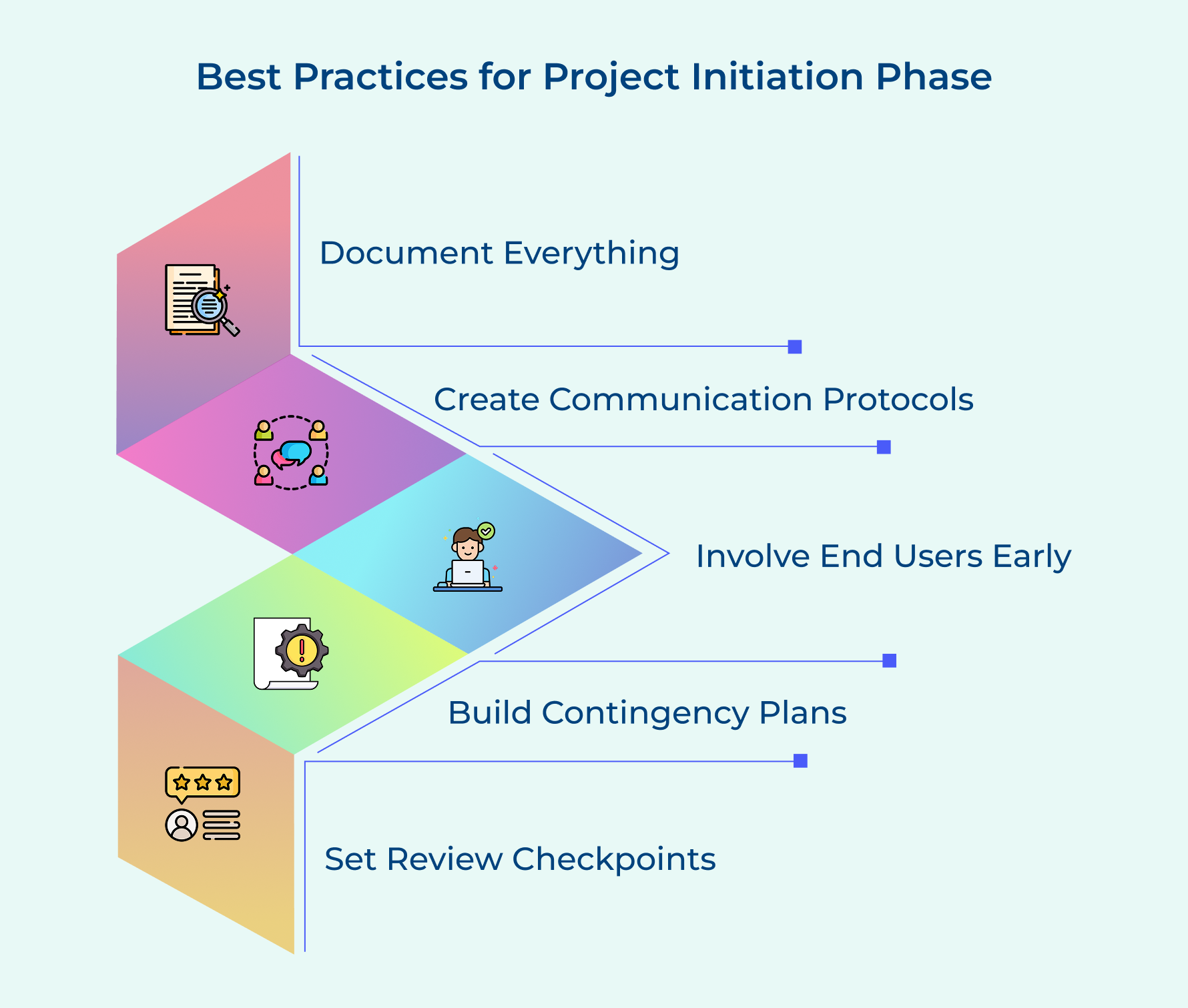
Best Practices for Project Initiation Phase
These best practices complement the standard initiation steps and help project managers avoid common pitfalls that derail projects before they truly begin.
1. Document Everything in Writing
During project execution, relying on verbal agreements is risky. Written documentation keeps everyone on the same page, creates accountability and avoids misunderstandings later.
2. Involve End Users Early in Planning
Don’t wait until delivery to think about the people using your end product. Bringing end users in early uncovers true needs, not assumptions while improving adoption once the project is complete.
3. Create Communication Protocols and Standards
Clear communication plans keep project execution smooth. Set rules for how and when updates are shared so teams stay aligned as well as informed.
4. Build Contingency Plans for Major Risks
Strong risk management means preparing for the unexpected. Identify possible issues early, plan your responses and keep progress steady even when challenges hit.
5. Set Regular Review Points and Checkpoints
Schedule checkpoints to keep work on track. Reviews give teams a chance to adjust course and stakeholders can catch potential issues before they escalate.
Challenges Faced During Project Initiation
Project initiation often feels like trying to solve a puzzle with missing pieces. These common challenges can derail projects before they even begin.
Unclear or Conflicting Business Requirements
Stakeholders often struggle to articulate what they actually need versus what they think they want. Multiple departments may have competing priorities that create confusion about the project’s true purpose and expected outcomes.
Inadequate Stakeholder Engagement and Buy-in
Key decision-makers frequently remain too busy to participate meaningfully in initiation activities. This lack of engagement leads to assumptions about requirements and creates approval delays that frustrate project teams as well as the entire schedule.
Unrealistic Timeline and Budget Expectations
Organizations often underestimate the complexity and resources required for successful project delivery. Pressure to start quickly leads to rushed planning that sets unrealistic expectations and creates inevitable disappointment when reality emerges.
Insufficient Authority and Decision-Making Power
Project managers sometimes lack the organizational authority needed to make critical initiation decisions. This power gap creates bottlenecks when approvals are needed and undermines the project manager’s ability to drive the initiation process forward effectively.
Each solution addresses specific pain points that experienced project managers encounter regularly.
- Conduct structured stakeholder interviews to clarify and document business requirements systematically rather than relying on assumptions.
- Schedule dedicated stakeholder workshops with clear agendas and defined outcomes to ensure meaningful participation from busy executives.
- Use historical project data and expert judgment to create realistic estimates that account for complexity as well as organizational constraints.
- Establish clear escalation paths and decision-making protocols that empower project managers to resolve issues without constant approval delays.
- Create visual project roadmaps and prototypes that help stakeholders understand complexity before committing to timelines or budgets.
Project Initiation as Your Foundation for Success
Project initiation acts as the foundation that determines if your projects will succeed or fail before you even begin execution. Think of it as building a house – without a solid foundation, even the most beautiful structure will eventually crumble under pressure.
Proper initiation directly impacts your bottom line by preventing costly scope changes, reducing project overruns and improving client satisfaction through clear expectations. This structured approach enhances operational efficiency while building stronger client relationships that generate repeat business and referrals for sustained growth.
Limit time — not creativity
Everything you need for customer support, marketing & sales.
Pooja Deshpande is a content contributor at Kooper, focused on creating insightful resources that help agencies and service providers scale efficiently. Passionate about SaaS trends, content strategy, and operational excellence, she delivers practical, easy-to-implement guidance for modern business leaders.