Practical Project Scheduling Techniques for Real-World Projects
- What is a Project Scheduling Technique?
- 10 Essential Techniques for Effective Project Scheduling
- Key Benefits of Project Scheduling in Project Management
- Best Practices for Developing an Effective Project Schedule
- The Road Ahead: Leveraging Scheduling for Project Triumph
- FAQs about Project Scheduling Techniques

Key Highlights:
- Project scheduling techniques help align multiple projects by balancing resource allocation while also ensuring effective management.
- Modern tools enable teams to track project progress instantly, making adjustments and maintaining transparent communication with stakeholders.
- Scheduling frameworks highlight critical path tasks. Thus, focusing resources on high-impact work.
Are your projects consistently falling behind schedule, leaving your team scrambling to meet deadlines? You’re not alone.
The constant juggling of resources, shifting priorities, and unexpected roadblocks can make project management feel like navigating through a maze blindfolded.
Mastering project scheduling techniques can transform this chaos into clarity. From traditional Gantt charts to modern Agile methodologies, these proven scheduling approaches provide the structure and visibility needed to meet project deadlines successfully.
Let’s explore some of the powerful scheduling techniques that will help you take control of your project timelines and exceed stakeholder expectations.
What is a Project Scheduling Technique?
A project scheduling technique refers to a method used to plan as well as manage the timing of tasks, resources, and milestones within a project. The technique helps define when each task will be performed, who is responsible, and how long each step will take.
Common project scheduling techniques include Gantt charts, Critical Path Method (CPM), and Agile frameworks, all of which offer unique advantages for project planning as well as execution.
A project scheduling technique provides a strategic approach to avoid these issues and drive project success.
Primary objectives:
- Timeline optimization: Ensure efficient use of time by properly sequencing activities and minimizing idle periods between tasks.
- Resource allocation: Distribute human capital, tools, and other resources effectively across various project activities along with concurrent projects.
- Risk management: Identify potential scheduling conflicts, dependencies, and constraints early to prevent project delays.
10 Essential Techniques for Effective Project Scheduling
Effective project scheduling is key to delivering projects on time and within scope. These techniques ensure individual tasks are streamlined and goal-aligned.
1. Gantt Chart
A Gantt chart is like a horizontal bar chart that gives you a bird’s-eye view of your project. It maps out tasks across a timeline, showing how long each one will take and where they depend on each other. It’s especially useful for complex projects with lots of moving parts and stakeholders.
Gantt chart helps spot timing conflicts, manage resources, and stay on top of deadlines. It is especially handy for client-facing projects where everyone needs a clear picture of what’s happening and when.
To create one, you can use a spreadsheet or specialized tools like TeamGantt or Microsoft Project. Start by listing tasks, their durations, dependencies, and key milestones.
Tips:
- Color-code different project phases or teams to make the chart instantly scannable and facilitate quick status updates.
- Schedule regular (weekly) updates to maintain accuracy and use it as a communication tool in client meetings.
- Keep it updated regularly to reflect real progress and any changes along the way.
2. Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a smart way to pinpoint the longest sequence of dependent tasks in your project. It shows which tasks absolutely cannot be delayed without affecting the overall completion date, helping you manage timelines effectively.
The given method is a lifesaver for agencies juggling multiple client projects with tight deadlines. It highlights which tasks have flexibility (float) and which don’t, ensuring you allocate resources wisely.
Start by listing all activities, their durations, and dependencies. Use forward and backward passes to identify the critical path as well as task flexibility.
Tips:
- Focus extra resources on critical path tasks to prevent project delays.
- Build in small buffers for critical path activities to account for unexpected client feedback or revisions.
3. Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
A statistical tool using three-time estimates (optimistic, most likely, pessimistic) to calculate realistic project durations. Particularly useful for projects with uncertainty.
Agencies deal with varying client requirements and uncertain creative processes. PERT provides more accurate time estimates, helping manage client expectations and resource allocation more effectively.
For each task, gather three-time estimates from experienced team members. Use the PERT formula [(O + 4M + P)/6] to calculate the expected duration. Create a network diagram showing task relationships.
Tips:
- Include team members from different disciplines when estimating times to get more accurate ranges.
- Adjust estimates based on historical project data to improve future accuracy.
4. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) helps break big projects into smaller, manageable task lists.
For example, if you’re building a website, start with main deliverables like design, development, and testing, then break them down—design becomes wireframes, mockups, as well as revisions.
The approach ensures nothing is missed while making assigning tasks, estimating timelines, and tracking progress much easier. Use a visual hierarchy to show how all tasks fit together logically.
Tips:
- Use the 100% rule – ensure WBS includes all work necessary to complete the project.
- Keep work packages small enough to be estimated and assigned to specific team members.
5. Agile Sprints Scheduling
Agile sprints are short, fixed-length development cycles (usually 1-4 weeks) where specific tasks are planned, executed, and reviewed. It allows for flexible adaptation to changing requirements.
The scheduling technique is perfect for agencies handling dynamic client projects with evolving requirements. It enables regular client feedback, quick pivots, and continuous improvement while maintaining a productive workflow.
Define sprint length, hold planning meetings to select tasks from the backlog, execute work, and end with review meetings.
Tips:
- Keep sprints short (2 weeks max) to maintain flexibility and quick feedback loops.
- Set clear sprint goals and protect the team from scope changes during a sprint.
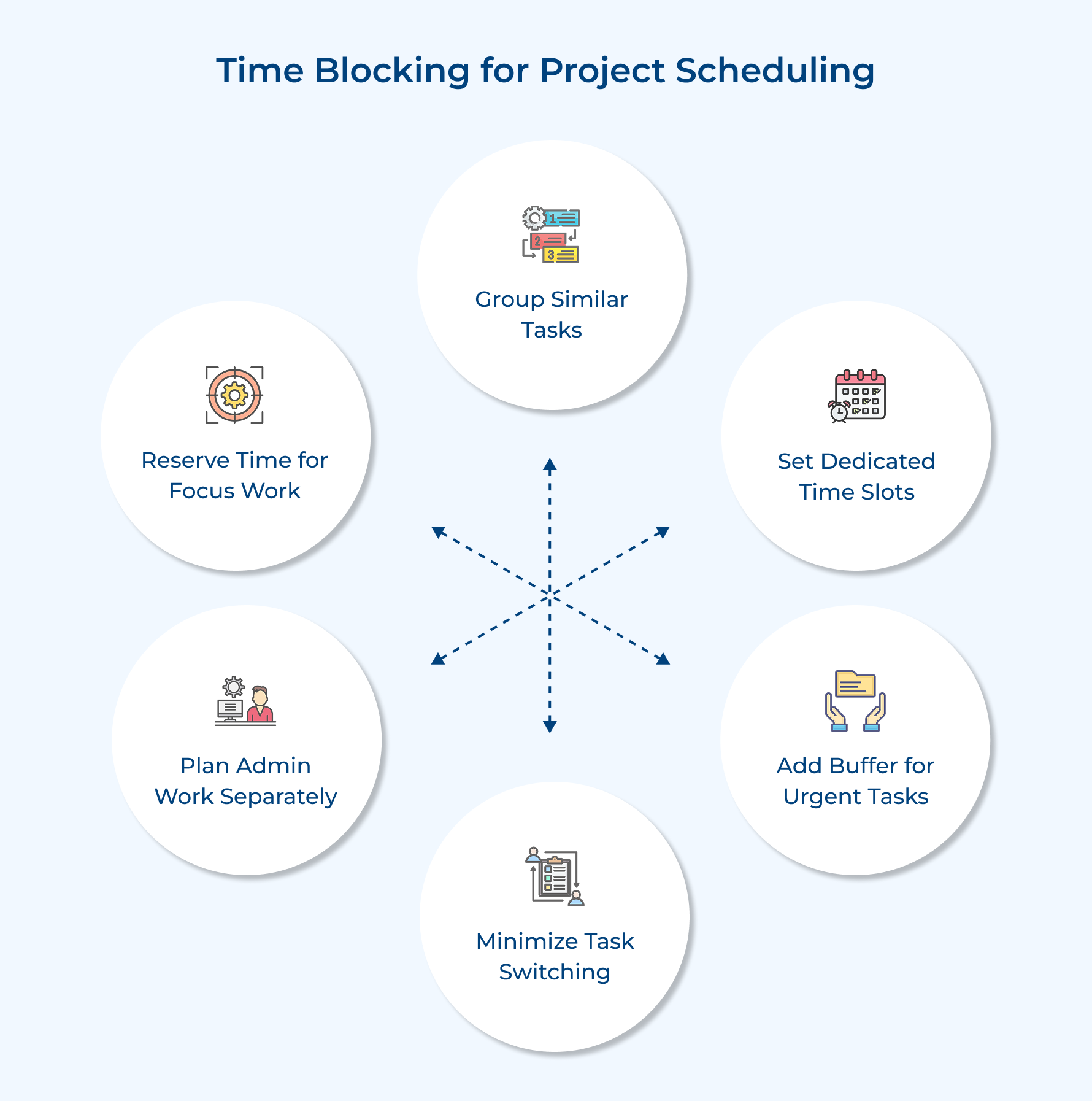
6. Time Blocking
Time blocking is a great way to manage your day by assigning specific tasks to set time slots. It’s perfect for agency pros juggling multiple client projects!
For instance, dedicate your mornings to deep-focus client work, block afternoons for meetings, and leave some time for admin tasks.
The blocking method helps you stay productive, avoid constant task-switching, and ensure everything gets its due attention.
Tips:
- Block similar tasks together to minimize context switching and maximize efficiency.
- Include buffer time between blocks for unexpected urgent client requests.
7. Kanban Scheduling
Kanban is a visual representation system that keeps your workflow organized and transparent. Picture a board with columns like “To Do,” “In Progress,” “Review,” and “Done.”
Tasks are represented as cards that move through these stages. It’s perfect for agencies, offering clear visibility into task progress, bottlenecks, and team capacity.
Set WIP (work-in-progress) limits to prevent overload as well as keep things running smoothly. Simply create your board, add tasks as cards, and move them along as you work.
Tips:
- Set and strictly enforce WIP limits to prevent overloading team members.
- Use swimlanes to separate different clients or project types for better organization.
8. Resource-Leveling Scheduling
Resource leveling helps resolve conflicts and prevent overallocation by adjusting task timings without extending the project timeline.
It is great for balancing workloads in agency teams, ensuring consistent quality while avoiding bottlenecks.
If someone’s overloaded, you can reschedule tasks using available float or share the work with others. It keeps your team energized, prevents burnout, and ensures smooth progress on all deliverables.
Review resource allocation weekly to identify and prevent potential bottlenecks. Cross-train team members to increase scheduling flexibility.
9. Milestone-Based Scheduling
Milestone planning focuses on key project checkpoints or deliverables, breaking the work into major phases with clear goals. It’s perfect for agencies to communicate progress, align with clients, and maintain momentum.
Set realistic dates for milestones, considering dependencies and resources. Milestones also provide ideal points for reviews, approvals, and billing, ensuring everyone stays on track.
Include buffer time before client-facing milestones to ensure quality control. Use milestones as natural points for client billing and project status reviews.
10. Resource Calendar
A resource calendar maps out team availability, including vacations, training, and other commitments. It’s a must-have for realistic project planning, helping agencies avoid overallocation and support work-life balance.
Regularly update the calendar with planned absences as well as admin time, and use it to schedule project tasks effectively. This way, you’ll keep projects on track while ensuring your team stays productive and balanced.
Key Benefits of Project Scheduling in Project Management
Project scheduling provides structure and clarity, enabling teams to manage resources as well as deadlines efficiently. Let’s learn how it benefits project management in the long run.
- Improved Project Portfolio Management
Project scheduling provides visibility into resource allocation, timelines, and dependencies, helping align multiple projects effectively. Managers can balance workloads, ensuring optimal portfolio performance.
- Real-Time Tracking of Milestones
With modern tools, teams can instantly track progress, spotting delays or successes. Quick decision-making and proactive adjustments help maintain project momentum as well as transparent communication.
- Reduced Risk of Budget Overruns
Smart scheduling connects timeline changes to budget impacts, enabling early detection of cost issues. Teams can optimize resource allocation, preventing costly last-minute adjustments.
- Enhanced Forecasting Capabilities
Scheduling tools use historical data to create more accurate plans. Teams can make realistic estimates and anticipate challenges based on past performance.
- Better Task Prioritization
Scheduling frameworks highlight critical path tasks, allowing teams to focus resources on high-impact work first. It prevents bottlenecks and ensures smooth project flow.
Best Practices for Developing an Effective Project Schedule
Creating an effective project schedule is essential for ensuring smooth project execution. Here are best practices to help optimize resource use, minimize risks, and keep projects on track.
- Define Clear Project Scope and Objectives
Before diving into scheduling, make sure to map out project requirements, deliverables, and success criteria with your team as well as stakeholders. Document assumptions and constraints that could impact the timeline while also including measurable outcomes to track progress effectively.
- Build in Buffer Time
Leave reasonable time buffers between key milestones and tasks. Account for unexpected delays, feedback cycles, and resource constraints without overinflating your project timeline.
- Use Historical Data and Expert Input
Use past project data to estimate task durations. Consult your team members for accurate time estimates and consider learning curves for new team members or tasks.
- Maintain Schedule Flexibility
Design your schedule to allow minor adjustments without throwing the whole project off track. Create task groups that can adapt as project needs change.
- Use Appropriate Tools and Technology
Select scheduling tools that fit your project’s complexity. Make sure everyone has access and proper training while integrating these tools with your project management software for smoother workflows.
- Set Realistic Resource Allocations
When assigning tasks, consider your team’s availability, skills, and other commitments like holidays. Plan for potential resource conflicts and have backup strategies in place.
- Establish Regular Review Points
Schedule regular check-ins to track progress and make adjustments. Include specific times for stakeholder reviews and approvals, while allowing time for quality checks as well as testing.
- Plan for Risk Management
Identify risks that could impact your schedule and have mitigation plans in place. Account for external factors and develop contingency plans for major risks.
The Road Ahead: Leveraging Scheduling for Project Triumph
The journey to project scheduling mastery is an ongoing process of learning, adapting, and improving. Whether you choose Gantt charts for their visual clarity, embrace Agile sprints for flexibility, or combine multiple techniques—each approach brings unique strengths to your project management toolkit. The real power lies not in the techniques themselves, but in how you apply them to solve real-world challenges.
Take action now by evaluating your current scheduling practices and identifying areas for improvement. Start implementing these techniques incrementally, measure their impact, and adjust as needed.
Remember, even small improvements in project scheduling can lead to significant gains in productivity, team satisfaction, and project outcomes. Your path to more efficient, predictable, and successful project delivery starts with that first step toward better scheduling practices.
Limit time — not creativity
Everything you need for customer support, marketing & sales.
Pooja Deshpande is a content contributor at Kooper, focused on creating insightful resources that help agencies and service providers scale efficiently. Passionate about SaaS trends, content strategy, and operational excellence, she delivers practical, easy-to-implement guidance for modern business leaders.