What is Cost Variance in Project Management? Formula & Examples
- What is Cost Variance in Project Management?
- Importance of Project Cost Variance
- How to Calculate Cost Variance in Project Management?
- Causes of Project Management Cost Variance
- Tips for Efficient Cost Variance Management in Projects
- Types of Cost Variance in Project Management
- Cost Variance Tracking – The Key to Smarter Project Management
- FAQs about Cost Variance in Project Management

Key Highlights:
- Cost variance in project management measures the difference between budgeted and actual costs, showing if a project is under or over budget.
- Primary causes include inaccurate cost estimates and scope creep, leading to unexpected budget increases during projects.
- Use real-time tracking and regular reviews to identify variances early while keeping projects financially on track.
Cost variance in project management can quietly drain profits if you don’t track it closely. Many teams realize too late that spending has already gone beyond the plan, leaving them scrambling to explain overruns and request more budget.
The key is catching these issues early. By regularly monitoring cost variance, you can spot warning signs, understand where money is slipping and take action before problems snowball.
Instead of stressful last-minute fixes, you gain predictable outcomes and stronger client trust. This guide shows you how to calculate, analyze and manage cost variance to keep every project financially healthy.
What is Cost Variance in Project Management?
Cost variance measures the difference between your project’s budgeted costs and actual expenses. When actual costs exceed the budget you have a negative variance that signals overspending. When actual costs fall below budget you achieve a positive variance indicating cost savings. This metric serves as your financial compass throughout project execution.
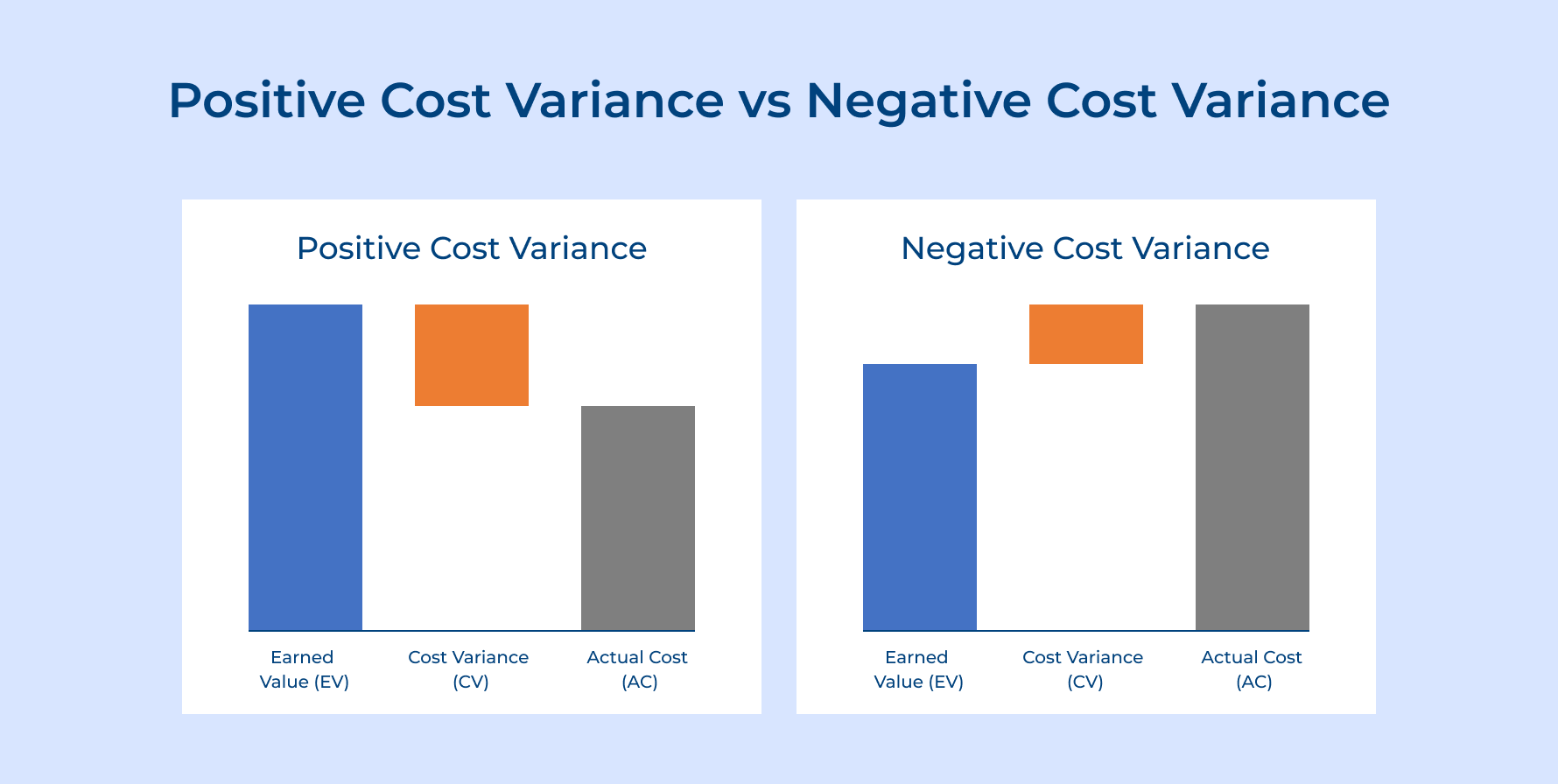
Positive Cost Variance vs Negative Cost Variance
Positive cost variance indicates you’re spending less than budgeted which typically signals good cost control or project efficiency gains. However positive variance might also reveal scope reductions or quality shortcuts that could impact final deliverables and client satisfaction.
Negative cost variance shows actual spending exceeds your budget which raises immediate concerns about profit margins and project viability. While negative variance often indicates problems it might result from legitimate scope expansions or necessary quality improvements that add client value.
Key objectives:
- Resource allocation optimization: Track spending patterns to allocate team members and tools more efficiently across current as well as future projects.
- Profit margin protection: Monitor variances early to prevent budget overruns from eroding your project’s profitability completely.
- Client expectation management: Use variance data to communicate transparently about project costs and potential changes with stakeholders.
- Process improvement identification: Analyze variance trends to spot inefficiencies in your project workflows and delivery methods.
- Financial forecasting enhancement: Apply variance insights to create more accurate budgets and timelines for similar future engagements.
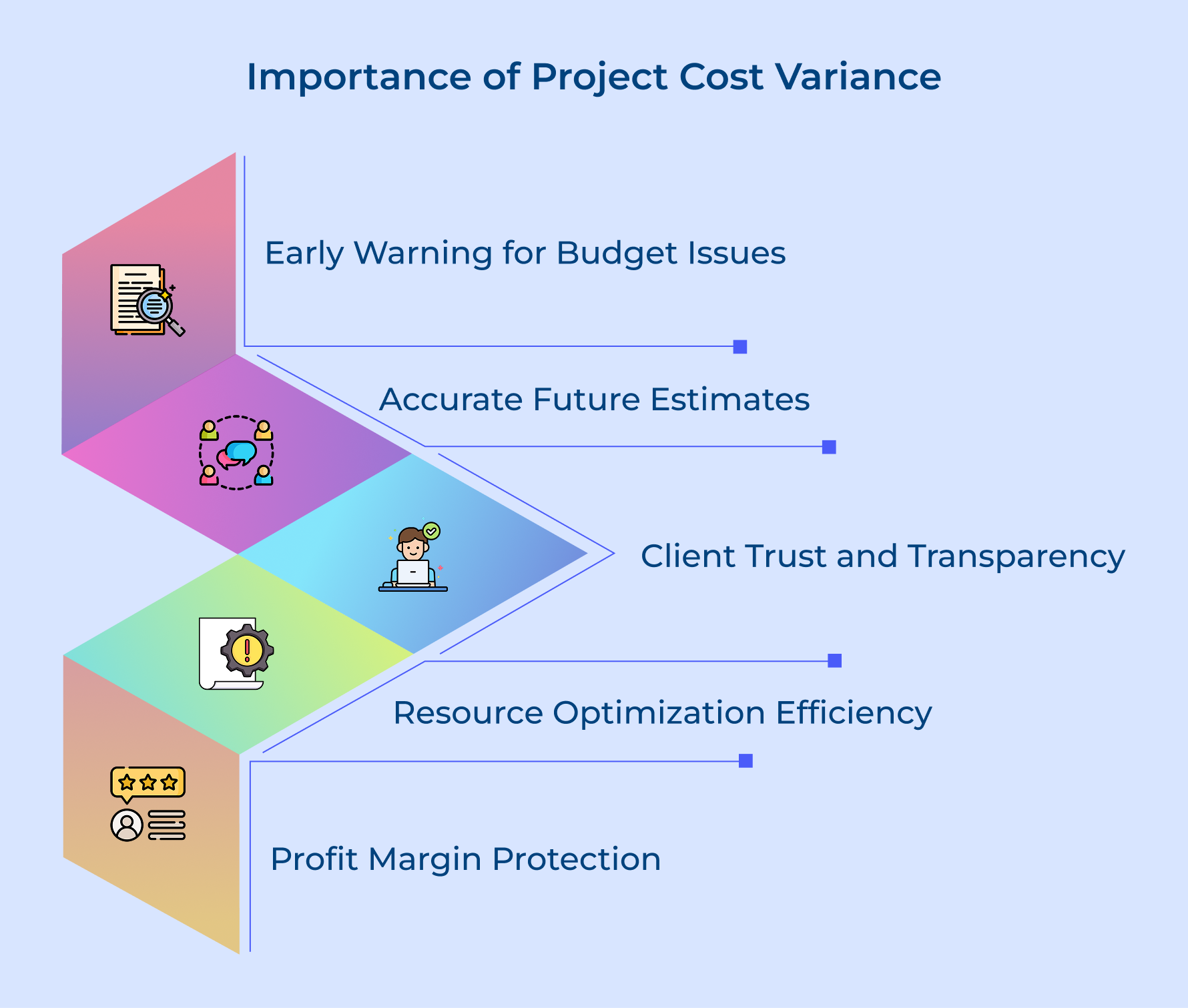
Importance of Project Cost Variance
Understanding cost variance helps project managers make informed financial decisions and maintain project health throughout the delivery cycle.
Early Warning System for Budget Issues
Cost variance works like an early alarm for your project schedule. It shows when spending starts to drift, giving you time to act before it turns into a big problem.
Foundation for Accurate Future Estimates
Tracking variance against the budget at completion helps you create more accurate estimates. Past data shows where costs go off track, making future planning more realistic.
Client Trust and Transparency Builder
Sharing variance reports builds client trust. They see how money is managed, which proves accountability and often leads to stronger, long-term relationships.
Resource Optimization and Efficiency Gains
Variance analysis shows which resources or processes stay within budget and which don’t. This helps you optimize allocation and improve team efficiency.
Profit Margin Protection Strategy
Monitoring cost variance against the budget at completion protects profit margins. Early action lets you adjust scope or timelines before losses escalate.
How to Calculate Cost Variance in Project Management?
Calculating cost variance is simple. You compare the planned budget with actual expenses to see if you’re over or under budget. This shows financial performance and highlights areas that need quick fixes.
Formula
Components:
- Budgeted cost: This represents the original amount you planned to spend on specific project activities or the entire project scope.
- Actual cost: This reflects the real money spent on project activities including labor hours and material expenses up to the measurement date.
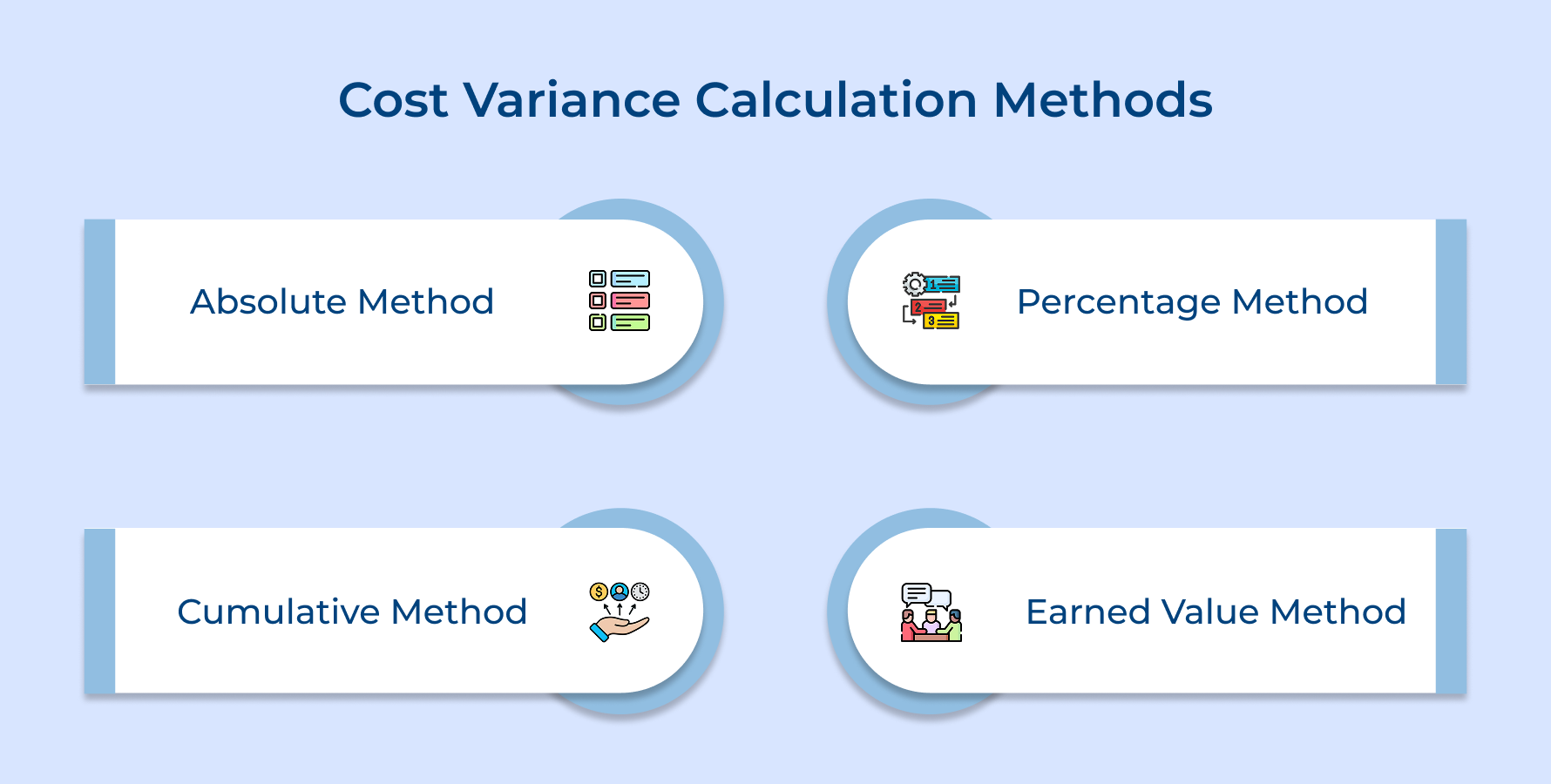
Cost Variance Calculation Methods
Different calculation approaches help project managers analyze cost performance from various angles depending on their specific reporting needs and stakeholder requirements.
1. Absolute Cost Variance Method
This straightforward approach subtracts actual costs from budgeted amounts to show exact dollar differences without any percentage context. The method reveals precise financial gaps but doesn’t indicate severity relative to project size.
Finance teams and executives prefer this method because it shows clear dollar impacts on bottom-line profitability as well as cash flow. Small projects might show minor absolute variances while large projects reveal significant dollar amounts that demand immediate management attention.
2. Percentage Cost Variance Method
It converts absolute differences into percentage terms to provide context about variance significance relative to total project budget. Percentage calculations help normalize comparisons across projects of different sizes and complexity levels.
Project managers use percentage variance to benchmark performance against industry standards and compare multiple projects objectively. This approach helps prioritize attention toward projects with the highest percentage deviations regardless of absolute dollar amounts involved.
3. Cumulative Cost Variance Method
This approach tracks total variance from project start to current measurement date rather than focusing on individual time periods. Cumulative tracking reveals overall project financial health and long-term spending trends that periodic measurements might miss.
Program managers overseeing multiple related projects rely on cumulative variance to assess overall portfolio performance and resource allocation effectiveness. This method helps identify systematic cost control issues that require organizational process improvements rather than project-specific interventions.
4. Earned Value Cost Variance Method
The advanced technique compares earned value against actual costs to measure cost efficiency of completed work rather than planned work. It provides more accurate performance insights by considering actual progress achieved rather than time-based budget expectations.
Sophisticated project management offices use earned value variance because it accounts for scope changes and schedule variations that affect cost performance. This method helps distinguish between cost overruns caused by inefficiency versus those resulting from accelerated delivery or expanded scope requirements.
Ideal Steps to Calculate Cost Variance
Follow these systematic steps to ensure accurate variance calculations that provide meaningful insights for project decision-making.
Step 1: Determine Project Budget Baseline: Establish your approved project budget including all planned costs for labor, materials, overhead and contingencies. This baseline becomes your reference point for all future variance calculations as well as performance comparisons.
Step 2: Track Actual Costs Incurred: Record all real expenses including direct labor hours, material purchases, equipment rentals and overhead allocations. Maintain detailed cost tracking systems that capture expenses as they occur rather than waiting for monthly summaries.
Step 3: Calculate Earned Value for Completed Work: Assess the budgeted cost of work that has been actually completed using objective completion criteria. This step requires honest evaluation of deliverable completion percentages based on predefined quality and acceptance standards.
Step 4: Apply Cost Variance Formula: Subtract actual costs from earned value using the standard formula to determine your current cost variance. Document the calculation date and project phase to maintain historical variance tracking for trend analysis.
Step 5: Analyze Results and Take Action: Interpret variance results within project context and develop corrective action plans for negative variances. Share findings with stakeholders and adjust future planning based on variance trends along with root cause analysis.
Standard Benchmark
Most successful projects maintain cost variance within plus or minus 10% of the earned value throughout the project lifecycle. This range allows for normal estimation uncertainty while preventing significant budget overruns that threaten project viability and stakeholder confidence.
Cost Variance Calculation Example
Let’s show you a straightforward cost variance calculation using a typical agency project that illustrates the key concepts in action.
Project Overview:
A social media marketing campaign for a local restaurant with content creation and advertising management over two months.
Budgeted vs Actual Costs:
- Original project budget: $45,000
- Actual expenses incurred: $47,200
- Cost difference requiring analysis
Basic Cost Variance Calculation:
- Cost Variance = Budgeted Cost – Actual Cost
- Cost Variance = $45,000 – $47,200
- Cost Variance = -$2,200**
Percentage Variance Analysis:
Percentage Cost Variance = [($45,000 – $47,200) / $45,000] × 100
Percentage Cost Variance = -4.89%**
Results Interpretation:
The negative $2,200 variance means the project went over budget by about 5%, which is at the higher end of acceptable limits. The extra cost came from adding more social media platforms requested by the client without updating the scope.
This shows how even small scope changes can affect project profitability. It also highlights why variance tracking is important for maintaining cost control and keeping client communication clear during the project.
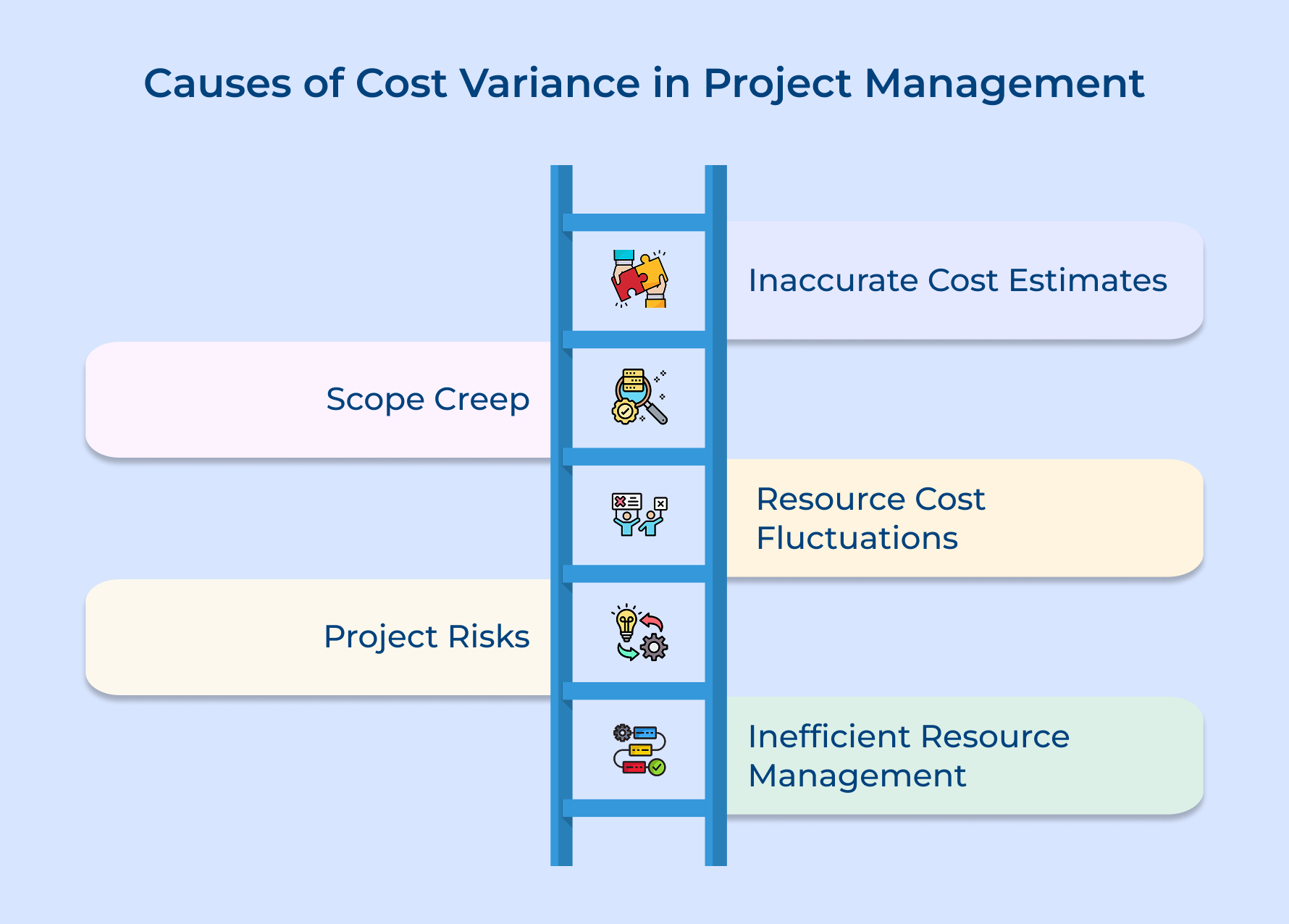
Causes of Project Management Cost Variance
Cost variances rarely appear without warning signs and understanding their root causes helps agency leaders implement preventive measures effectively.
Inaccurate Cost Estimates
Projects often start with incomplete information or optimistic assumptions about productivity and complexity. Without proper data, agencies underestimate delivery costs. Earned value analysis helps spot these gaps early by comparing actual progress with planned budgets.
Scope Creep
When clients request extra features without budget changes, costs rise quickly. Poorly defined project boundaries make this worse. Earned value analysis shows how scope creep affects both budget and progress in real time.
Resource Cost Fluctuations
Contractor rates or software fees can rise suddenly, straining budgets. Using earned value analysis, agencies can adjust forecasts and spot deviations from planned costs early.
Project Risks
Unexpected technical issues or staff changes often increase expenses. Earned value analysis highlights budget impacts of these risks quickly so managers can take corrective action.
Inefficient Resource Management
Assigning the wrong skills or constant task switching reduces efficiency. Earned value analysis shows how these choices inflate labor costs and delay schedules.
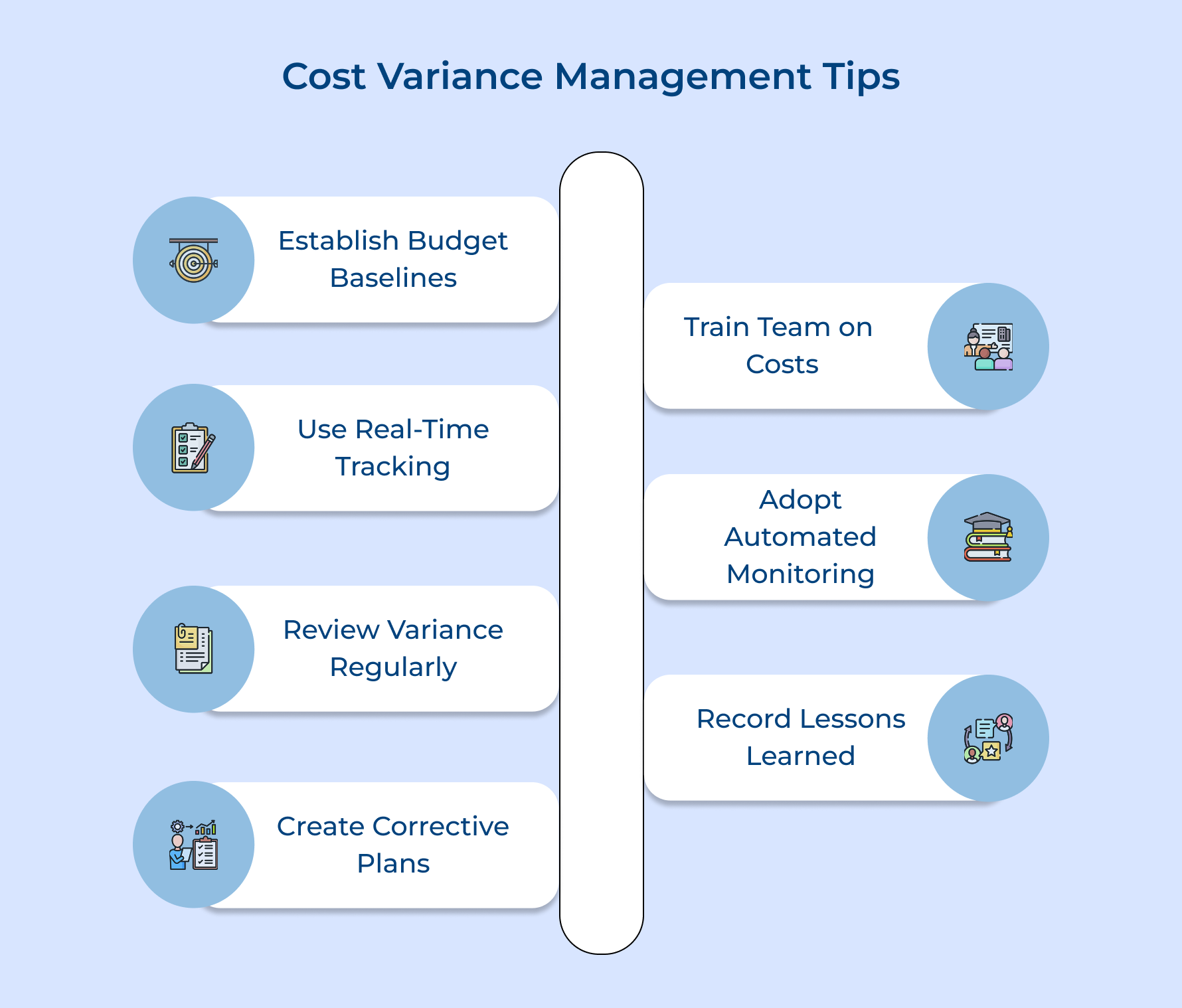
Tips for Efficient Cost Variance Management in Projects
Mastering cost variance management requires systematic approaches that transform financial chaos into predictable project outcomes.
1. Establish Robust Budget Baselines
A strong baseline budget creates the foundation for accurate tracking. It should include labor, materials, overhead and contingency reserves.
Key steps:
- Use historical data: Review similar projects to spot cost patterns and adjust estimates.
- Involve experts: Ask team leads and specialists to validate assumptions.
- Plan for risks: Keep a 10–20% contingency reserve for surprises.
A well-prepared baseline makes earned value analysis more accurate and useful.
2. Implement Real-Time Cost Tracking Systems
Tracking costs only at the end of the month is like checking your speed after the race is over. Real-time cost tracking gives managers instant visibility into spending, helping them make quick adjustments before problems escalate.
Ask yourself:
- Are you tracking costs daily or weekly?
- Does your system integrate with payroll and vendor payments?
- Can team members enter time and expenses easily?
- Do alerts notify managers immediately about overspending?
Real-time tracking shifts cost management from reactive firefighting to proactive financial control.
3. Conduct Regular Variance Analysis Reviews
Numbers lose their value if you don’t review them consistently. Regular variance analysis reviews keep teams aligned and uncover budget issues before they spiral out of control.
Common challenges:
- Meeting fatigue: Keep reviews short and focused; rotate leadership to maintain engagement.
- Data quality issues: Set reporting standards and train staff to submit accurate data on time.
These reviews transform raw numbers into meaningful insights that guide smarter project decisions.
4. Develop Proactive Corrective Action Plans
Spotting a variance is only half the battle, what matters is how quickly you respond. Corrective action plans give your team a clear roadmap to get projects back on track without delays.
Key elements to include:
- Escalation triggers: define when managers need to step in.
- Resource reallocation authority: allow swift shifting of talent or budget.
- Client communication protocols: keep clients informed before issues damage trust.
Teams spend less time worrying and more time executing solutions confidently, especially with proactive plans.
5. Train Team Members on Cost Awareness
Cost control isn’t just a manager’s responsibility, it’s a team effort. When everyone understands how their decisions affect profitability, variance prevention becomes much easier.
Questions to ask:
- Do team members know how their hourly rates impact profitability?
- Can they identify high-value vs. low-value activities?
- Are juniors trained to flag cost risks early?
- Do they understand trade-offs between scope, quality and budget?
Cost-aware teams naturally make smarter decisions that protect financial health.
6. Leverage Technology for Automated Monitoring
Manual tracking has its limits, but automation offers precision and speed. Smart tools can spot spending trends, predict overruns and alert managers instantly.
Best practices:
- Predictive analytics: forecast risks using historical and real-time data.
- Integration: connect software with accounting, payroll and time tracking.
- Custom alerts: match alerts to your organization’s tolerance levels.
Automation helps variance management to shift from tedious manual work to data-driven decision-making.
7. Document Lessons Learned for Future Projects
Every variance tells a story, but its value lies in capturing it for the future. Lessons learned help refine estimates, strengthen processes and prevent repeated mistakes.
Focus on documenting:
- Root causes: why the variance happened, not just the numbers.
- Solutions: what worked and what didn’t.
- Estimation adjustments: how insights can improve future project planning.
Over time, this builds organizational wisdom that strengthens cost control and competitiveness.
Types of Cost Variance in Project Management
Understanding different variance types helps project managers identify specific financial performance patterns and apply targeted corrective measures.
Schedule Variance
When projects miss deadlines, teams often need overtime or faster delivery of materials. These extra costs cause overruns even if the original budget was accurate.
Resource Rate Variance
Sometimes projects require more skilled team members than planned. Changes in contractor rates or salary increases can also raise costs without any scope changes.
Efficiency Variance
This variance shows the gap between expected productivity and actual performance. Costs rise when tasks take longer due to workflow issues or lack of skills.
Material Cost Variance
Budget deviations happen when material prices rise after estimation. Supply chain problems or vendor price changes often make projects more expensive.
Cost Variance Tracking – The Key to Smarter Project Management
Effective cost variance in project management transforms from reactive into proactive financial stewardship that protects profitability and client relationships. This systematic approach enables early problem detection and swift corrective action.
Mastering cost variance analysis creates competitive advantages through improved estimation accuracy and enhanced stakeholder confidence. Teams that embrace comprehensive variance management consistently deliver projects within budget while building organizational knowledge for future success.
Limit time — not creativity
Everything you need for customer support, marketing & sales.
Shivank Kasera is part of the marketing team at Kooper, where he focuses on building content that helps agencies and service providers grow. With a keen interest in SaaS, operations, and scalability, he translates practical insights into actionable resources for business leaders.