Effective Project Management Techniques for Successful Projects

Key Highlights:
- Optimize workflows with proven project management techniques like agile, scrum, and Gantt charts.
- Manage risks effectively using tools like risk matrix and earned value management.
- Ensure stakeholder satisfaction with structured yet flexible project management methodologies.
Managing projects can feel overwhelming, especially with tight deadlines, limited resources, and shifting priorities. Without the right strategies in place, things can spiral.
That’s where effective modern project management techniques come in—they offer a roadmap to keep everything on track.
Methods like Agile, Scrum, and Waterfall help teams stay organized as well as meet deadlines. They also help tackle common challenges, boost collaboration, and adapt to changes.
Let’s dive into these project management methodologies and how they ensure you deliver successful projects!
What are Project Management Techniques?
Project management techniques refer to the methods as well as strategies used to plan, execute, and control projects effectively. These techniques help project managers and teams navigate the complexities of a project, ensuring it is completed on time as well as within budget.
Different techniques focus on specific aspects of project management, such as time management, cost control, risk management, and resource allocation. Some popular techniques include Agile methodology, Waterfall, Critical Path Method (CPM), and Lean Project Management. The choice of technique depends on the project’s nature, complexity, and requirements.
Key objectives:
- Efficiency enhancement: Streamline project management process to optimize time, resources, and effort while reducing redundancy throughout the project lifecycle.
- Risk mitigation: Identify, assess, and manage potential risks as well as challenges proactively through structured approaches rather than reactive solutions.
- Quality assurance: Ensure consistent delivery of high-quality project outcomes by establishing standardized processes, checkpoints, and quality control measures.
- Stakeholder satisfaction: Meet or exceed stakeholder expectations by maintaining clear communication, delivering value consistently, and managing changes effectively.
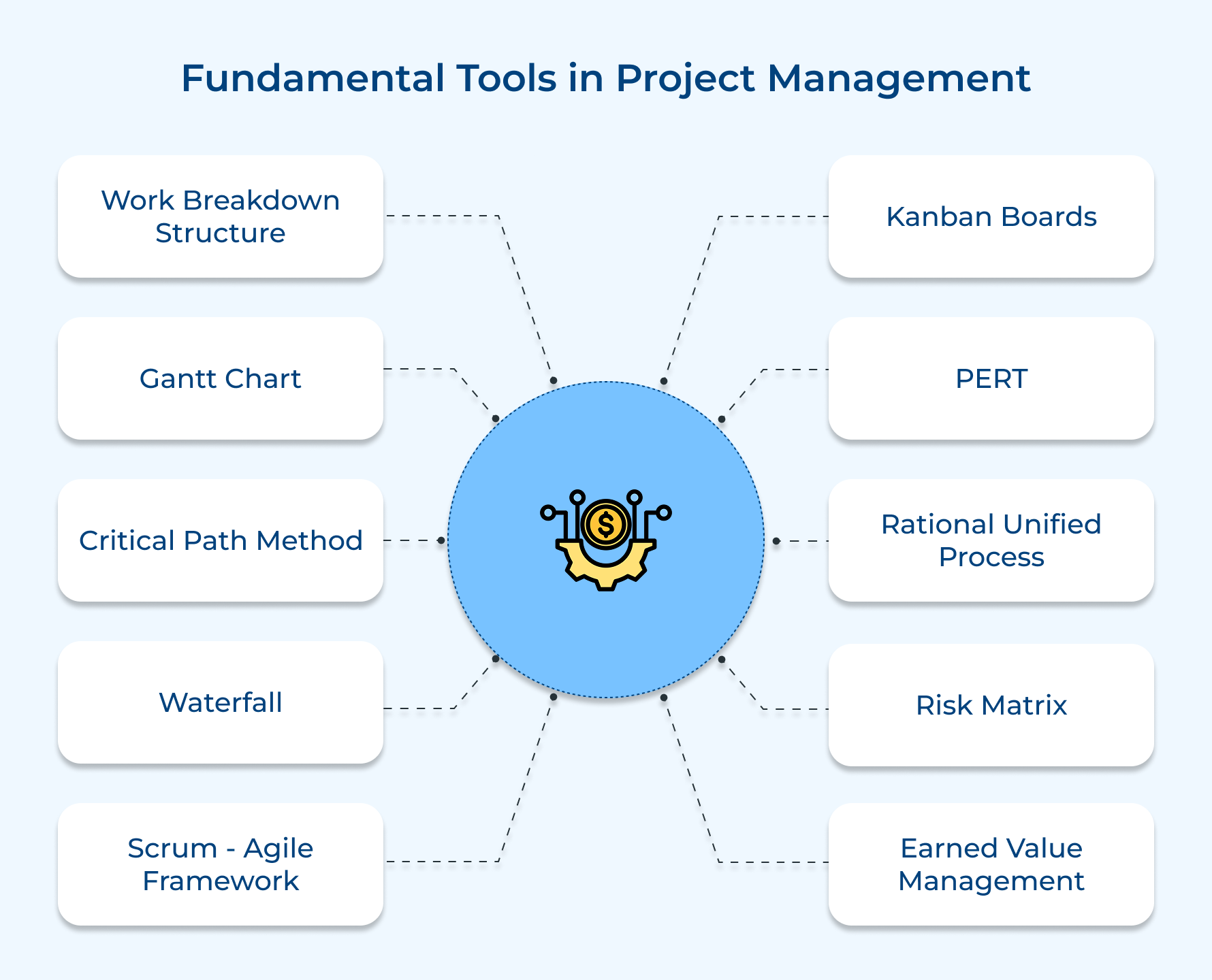
10 Fundamental Project Management Techniques and Tools
Effective project management relies on a solid toolkit to keep things on track. From planning to execution, these 10 fundamental tools and techniques are essential for ensuring your project’s success.
1. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) breaks down deliverables into smaller, manageable components. Think of it as a visual tree that organizes tasks and subtasks logically across different levels.
Here’s how WBS simplifies project management:
- Adds clarity and structure: Makes complex projects easier to digest.
- Covers the full scope: Ensures no task is overlooked.
- Boosts efficiency: It helps teams allocate resources, estimate costs, and track progress seamlessly.
How to create a WBS?
- Start with major deliverables.
- Break them down into smaller, actionable tasks.
- Organize everything visually for easy reference.
Tips for WBS success:
- 100% Rule: Capture all project work, including management and quality tasks.
- 8/80 Rule: Keep tasks manageable—no less than 8 hours, no more than 80 hours.
Your WBS is the foundation for planning, scheduling, and keeping projects on track!
2. Gantt Chart
Imagine planning a project where you can see every task lined up neatly on a timeline. That’s exactly what a Gantt chart does! It’s a horizontal bar chart that visually maps out tasks, their duration, dependencies, and the overall project schedule.
How Gantt charts simplify project management:
- Clear timelines: Easily spot when tasks start and end.
- Task relationships: See which tasks depend on others to avoid delays.
- Progress tracking: Monitor what’s done and what’s still pending.
How does it work?
Let’s say you’re organizing a product launch:
- List tasks: Create a marketing plan, design promotional materials, schedule the launch event, etc.
- Plot timelines: “Create marketing plan” might span a week, while “Design promotional materials” overlaps slightly and runs for two weeks.
- Track dependencies: The promotional materials can’t be finalized without the marketing plan, so you connect them.
3. Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method (CPM) identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks (known as the critical path) and shows the minimum time required to complete a project.
Focusing on task dependencies and float time (the wiggle room for non-critical tasks) helps CPM ensure that activities directly impact the project’s end date.
CPM prioritizes resources and minimizes delays by dividing workflow into manageable tasks. It helps teams pinpoint the tasks that need extra attention and highlights potential scheduling risks. This way, you can allocate resources smartly and keep your project on track.
How does it work?
Start by listing all project activities, their durations, and their dependencies. Then, calculate early start/finish and late start/finish dates for each task. The analysis reveals the critical path and shows where there’s flexibility (float time) for other tasks.
4. Waterfall
The Waterfall method is a step-by-step approach to the project management process where each phase is completed before moving to the next.
Think of it as progress flowing steadily in one direction—like a waterfall—through stages like requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and deployment.
Why should you choose this method?
The answer is simple. This method works best for projects with well-defined requirements where changes are costly or not feasible once the project is underway.
The said method offers a clear structure with thorough planning and documentation, making it ideal for industries like construction or manufacturing where precision is key.
Ideally, teams start with detailed requirements and get them approved before moving on to design. Each phase must be fully completed, with clear deliverables and sign-offs, before advancing. Thus making it easier to measure progress against the original plan.
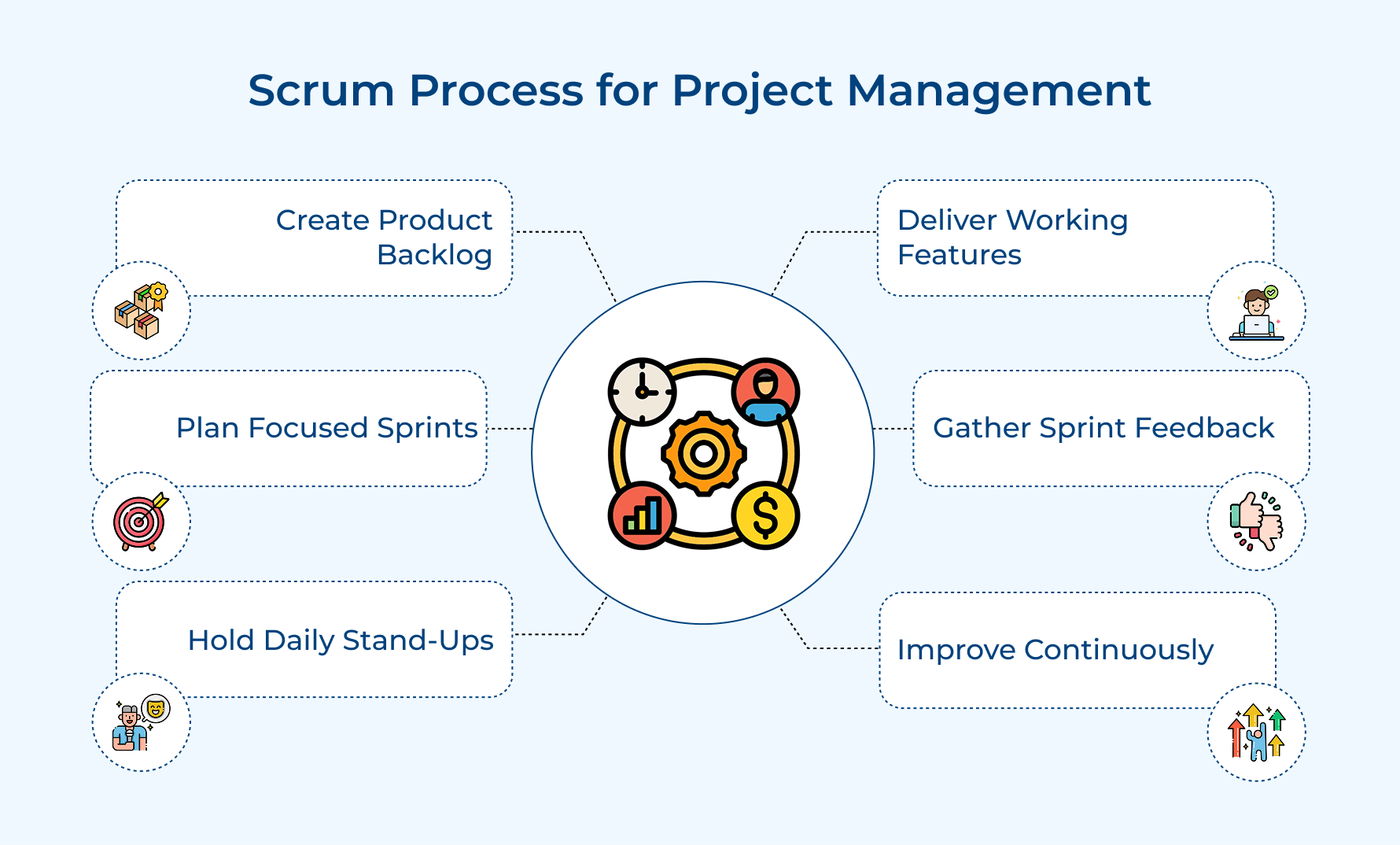
5. Scrum – Agile Framework
Scrum is an agile framework that breaks projects into short, fixed-length sprints (usually 2-4 weeks). It’s all about teamwork and adaptability, using daily stand-ups, sprint planning, reviews, as well as retrospectives to stay on track while delivering value incrementally.
Scrum shines when projects are complex, requirements keep changing, or regular feedback is essential. It helps teams respond quickly to changes, stay transparent, and deliver results in manageable chunks.
Let’s understand how Scrum works with an example. Imagine building a mobile app:
- Create a backlog: Start with a list of features like “User Login,” “Push Notifications,” and “Dark Mode.”
- Plan sprints: Pick the most important tasks, like “User Login,” for the first sprint. The team commits to delivering it by the end of two weeks.
- Work collaboratively: Each day, the team holds a 15-minute stand-up to share updates, tackle roadblocks, and stay aligned.
- Deliver and improve: At the end of the sprint, the team demonstrates the working login feature, gathers feedback, as well as discusses what went well and what could improve during the retrospective.
Tips for scrum success:
- Keep daily stand-ups short—15 minutes max is the golden rule.
- Regularly update your backlog with clear user stories and acceptance criteria to keep the team aligned.
6. Kanban Boards
A visual management tool that displays work items as cards moving through different stages of completion. It helps teams visualize workflow, limit work in progress, and identify bottlenecks.
Kanban provides real-time visibility into work progress and capacity. It helps teams maintain a steady flow, prevent overload, and continuously improve process efficiency through visual management.
Teams create boards with columns representing work stages. Cards move across columns as work progresses. Work-in-progress limits help maintain flow and identify process improvements.
7. PERT (Program Evaluation Review Technique)
A statistical tool for analyzing and representing the tasks in a project schedule. It uses three-time estimates (optimistic, most likely, pessimistic) to calculate realistic project completion times.
PERT helps manage uncertainty in project scheduling by considering multiple time scenarios. It provides more accurate time estimates and helps identify schedule risks in complex projects.
Teams gather three-time estimates for each task, calculate weighted averages, and create network diagrams. This helps determine expected durations and the probability of meeting deadlines.
8. Rational Unified Process (RUP)
RUP is an iterative framework for software development, organized into four distinct phases: inception, elaboration, construction, and transition. Each phase includes activities like business modeling, analysis, design, and testing.
Why use RUP?
- Structured yet flexible: Offers clear guidelines while adapting to changes.
- Risk management: Identifies and addresses risks early.
- Quality assurance: Focuses on iterative development to maintain high standards.
How RUP works:
- Inception: Define the project’s scope, goals, and initial requirements.
- Elaboration: Emphasize architecture and refine requirements, addressing major risks.
- Construction: Develop and test the system incrementally.
- Transition: Deploy the product to users and handle final adjustments.
9. Risk Matrix
A risk matrix is a visual tool used to evaluate and prioritize project risks based on their likelihood of occurring as well as their potential impact. It helps teams focus on the most critical threats.
Risk matrix uses:
- Systematic evaluation: Provides a structured approach to risk assessment.
- Resource allocation: Ensures risk management efforts target the highest-priority risks.
- Improved decision-making: Helps teams identify and address potential issues early.
How to use a risk matrix:
- Identify risks: List potential risks relevant to your project.
- Assess probability and impact: Evaluate how likely each risk is to occur and its potential consequences.
- Plot on the matrix: Place risks on a grid with axes for probability (low to high) and impact (low to high).
- Develop strategies: Create response plans for high-priority risks.
- Review regularly: Update the matrix monthly or when significant changes occur.
10. Earned Value Management (EVM)
A technique that measures project performance by comparing planned value against actual cost and earned value. It provides early warning signals for cost and schedule variances.
EVM helps teams objectively measure project performance and forecast future trends. It enables the early detection of problems and supports data-driven decision-making for project control.
The project team gets to track planned value, earned value, and actual cost regularly. They calculate performance indices and use them to forecast project outcomes as well as make corrections.
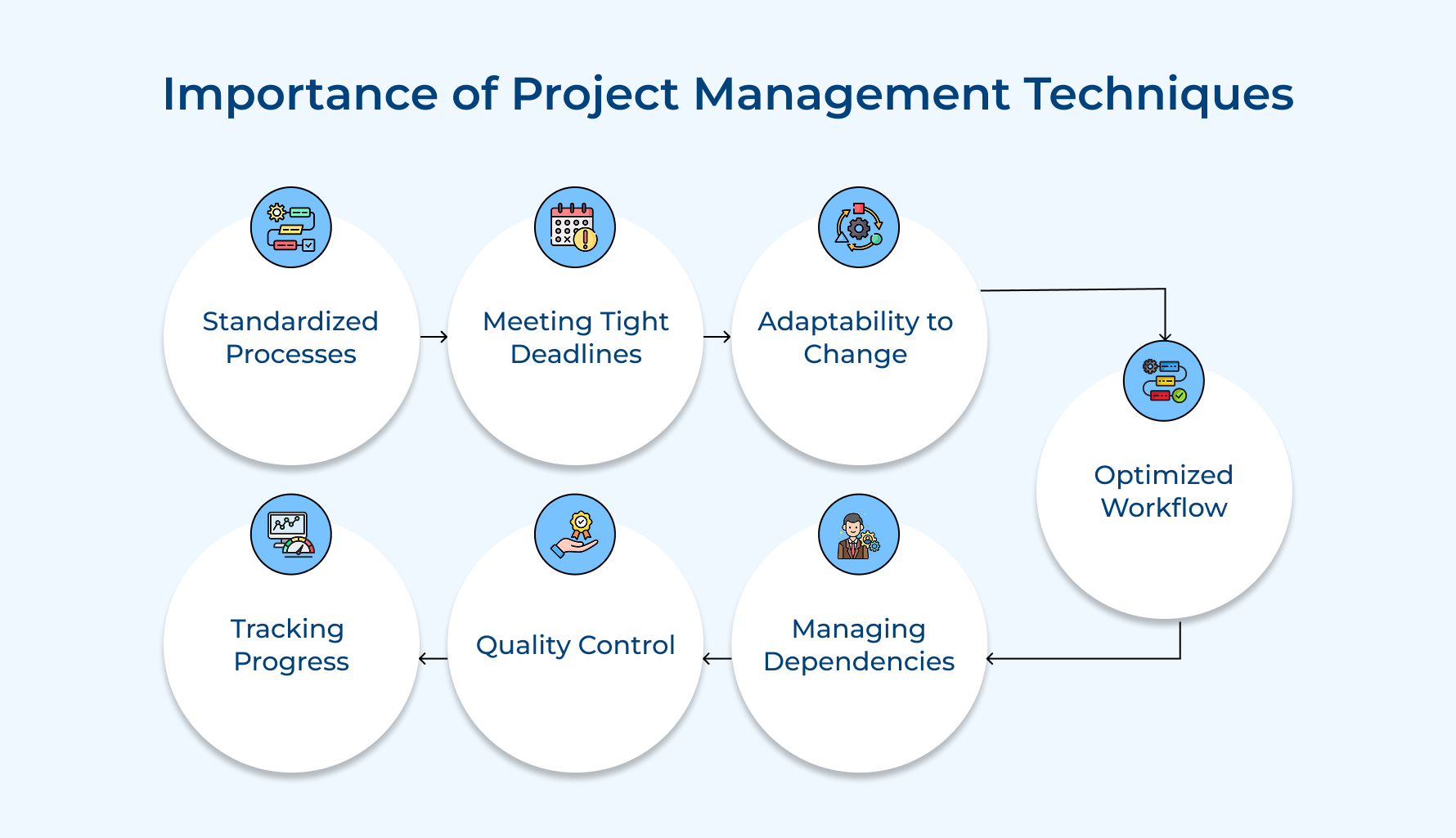
Why are Project Management Techniques Important?
Project management techniques are the backbone of any successful project. Let’s understand the importance of these techniques and how they help overall growth.
1. Standardized Processes
Structured techniques of project management ensure consistency across projects. By using common methods, teams understand their roles and responsibilities clearly, creating smooth workflows as well as aligned execution.
2. Meeting Tight Deadlines
Managing timelines is easier with the right tools! Breaking projects into smaller tasks, strategic resource allocation, and project tracking techniques help teams hit critical milestones without feeling overwhelmed.
3. Adaptability to Change
Change happens, and flexible frameworks make adapting easy. With clear systems for assessing as well as implementing changes, teams can stay on track while accommodating new priorities.
4. Optimized Workflow
Efficient workflows mean fewer bottlenecks and better productivity. By balancing workloads and eliminating unnecessary steps, teams can focus on what matters.
5. Managing Dependencies
Tracking interconnected tasks ensures that nothing falls through the cracks. Coordinating activities keeps everything moving smoothly from one phase to the next.
6. Quality Control
Quality isn’t left to chance. Regular checks and validation processes throughout the project ensure every deliverable meets expectations.
7. Tracking Progress
With real-time metrics and monitoring systems, teams can see where they stand, address issues early, and make data-driven decisions to keep the project on course.
Project Management Techniques for Lasting Success
Project management techniques are essential for completing projects successfully, on time, and within budget. Agile ensures flexibility, while Waterfall provides a more structured framework. Gantt charts and Kanban boards offer clear organization as well as effective tracking, helping teams stay focused.
Success emerges from combining appropriate techniques aligned with project requirements, team capabilities, and organizational goals. WBS offers scope clarity, Gantt charts enable timeline visualization, and Kanban optimizes workflows – each technique brings unique advantages to specific project challenges.
Project management tools and techniques act as catalysts for team collaboration, quality delivery, and continuous improvement. A thoughtful application of proven methods builds robust frameworks for consistent project success. Organizations leveraging well-chosen techniques build innovation and maintain competitive advantage.
Limit time — not creativity
Everything you need for customer support, marketing & sales.
Pooja Deshpande is a content contributor at Kooper, focused on creating insightful resources that help agencies and service providers scale efficiently. Passionate about SaaS trends, content strategy, and operational excellence, she delivers practical, easy-to-implement guidance for modern business leaders.