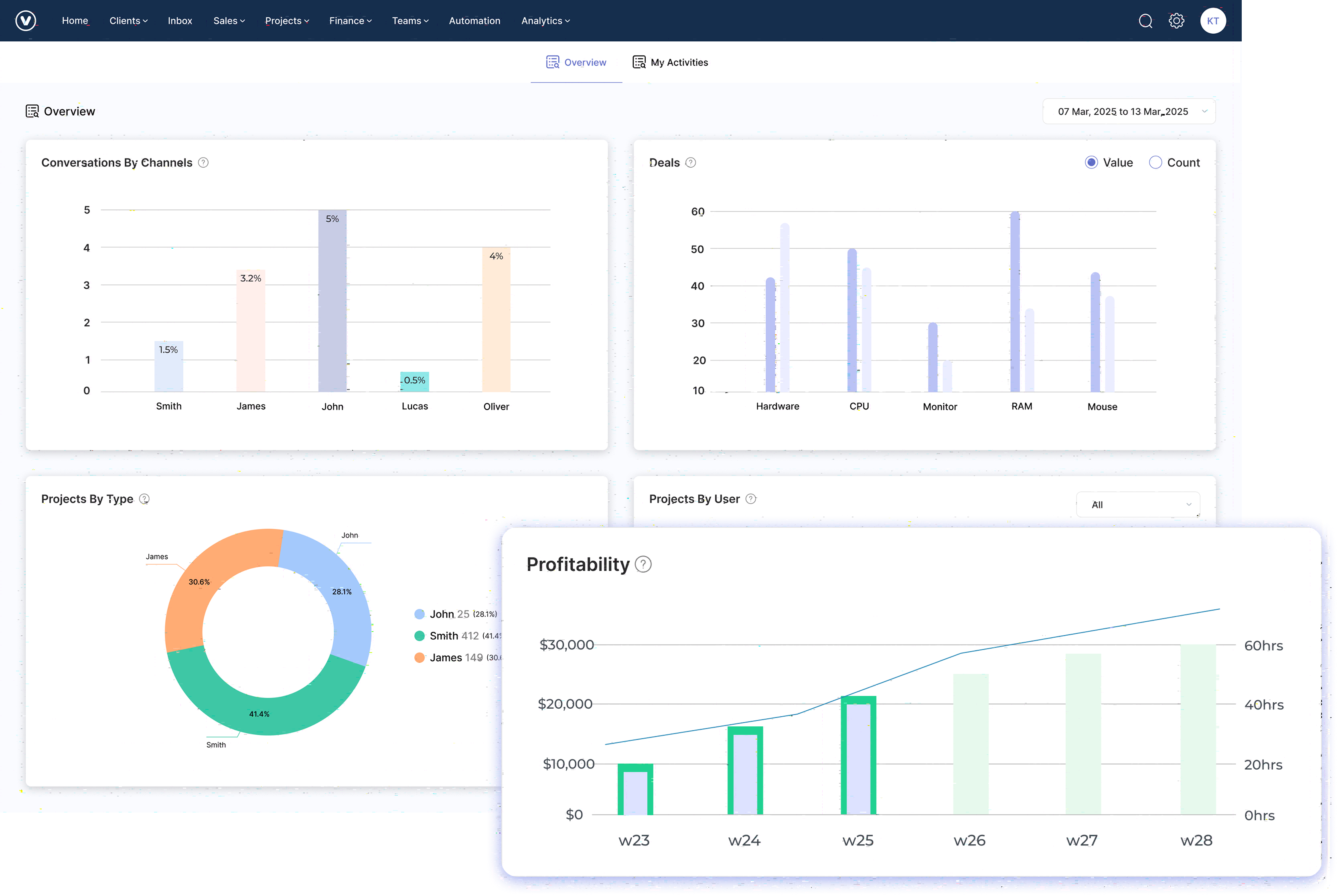
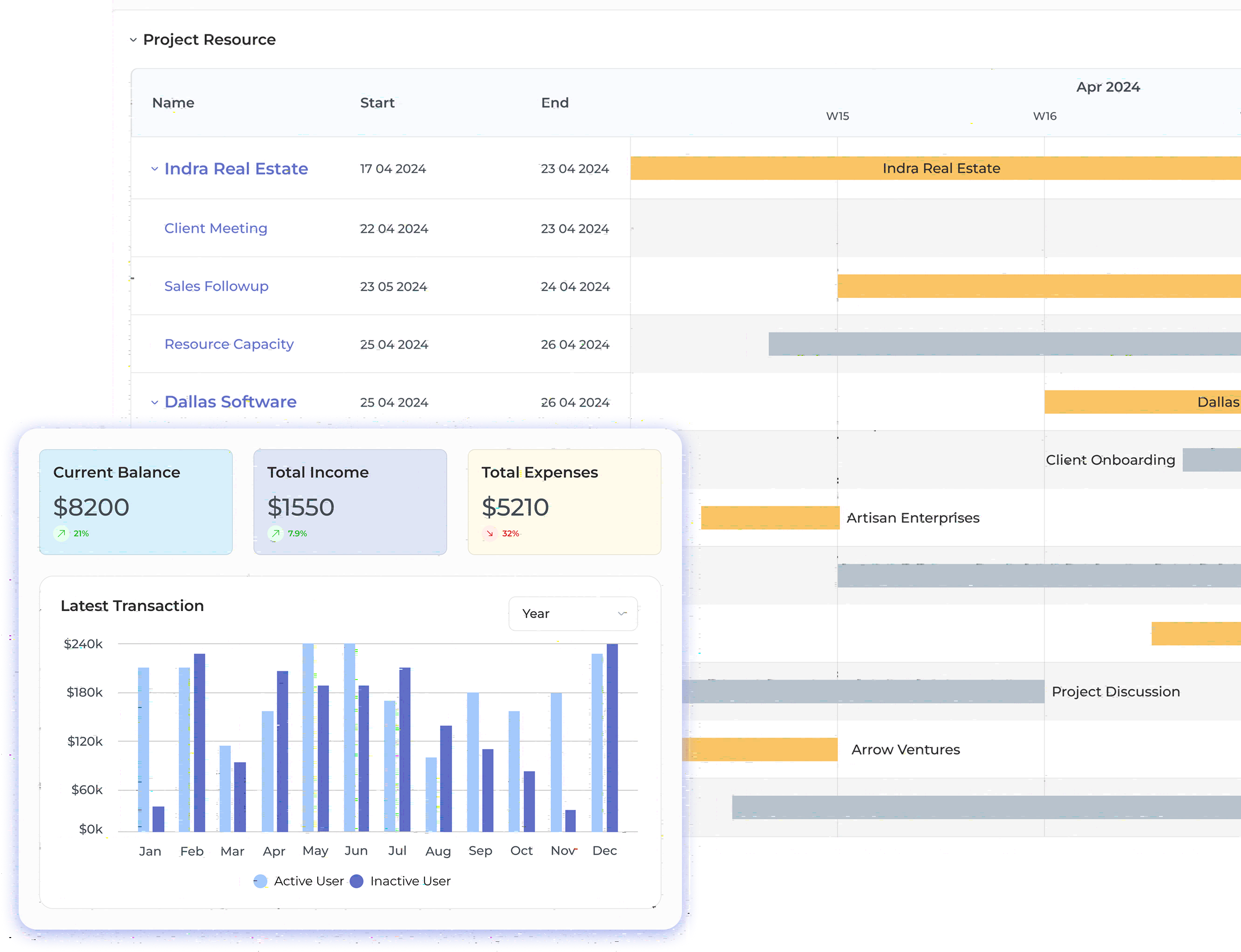
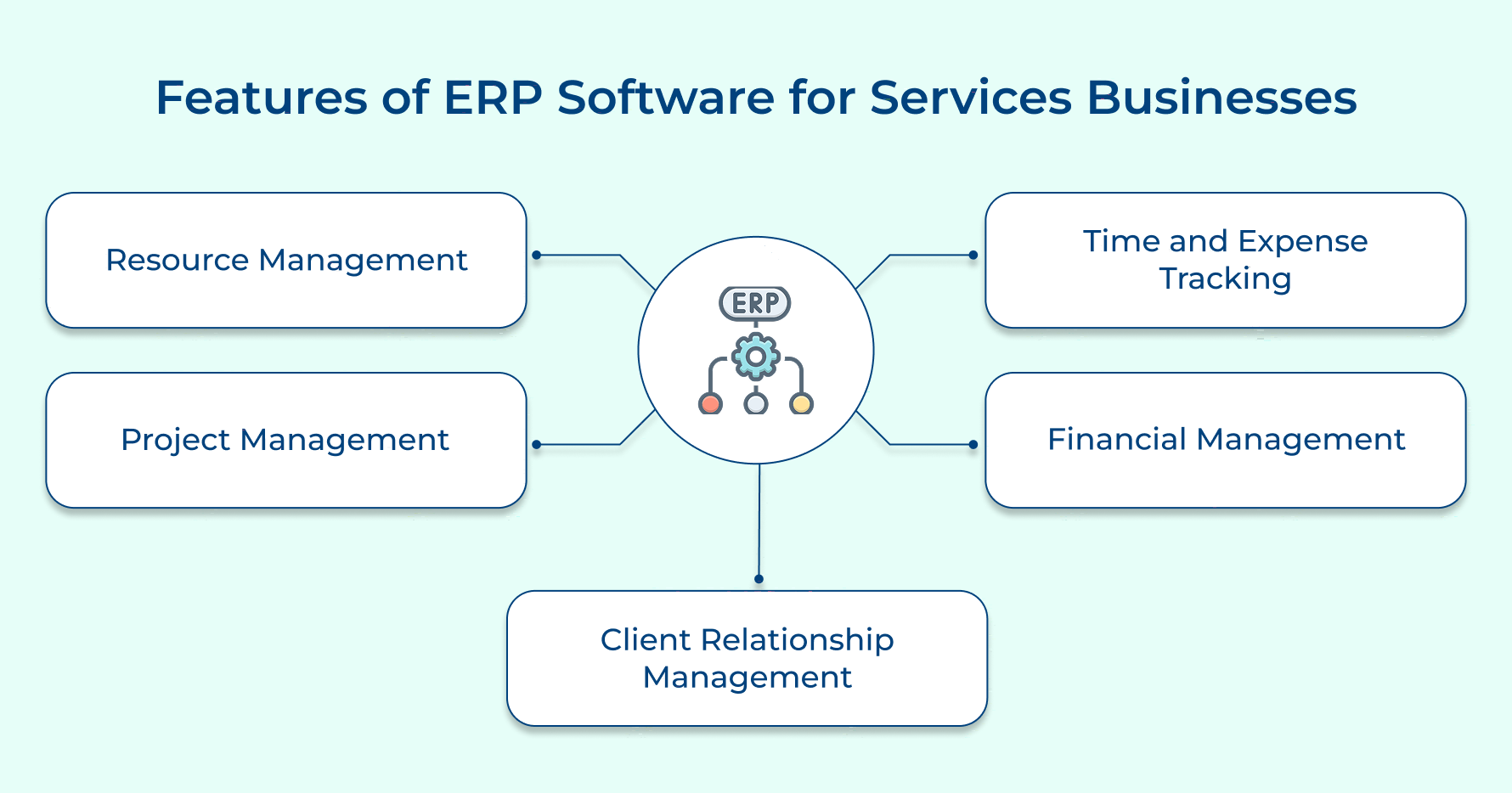
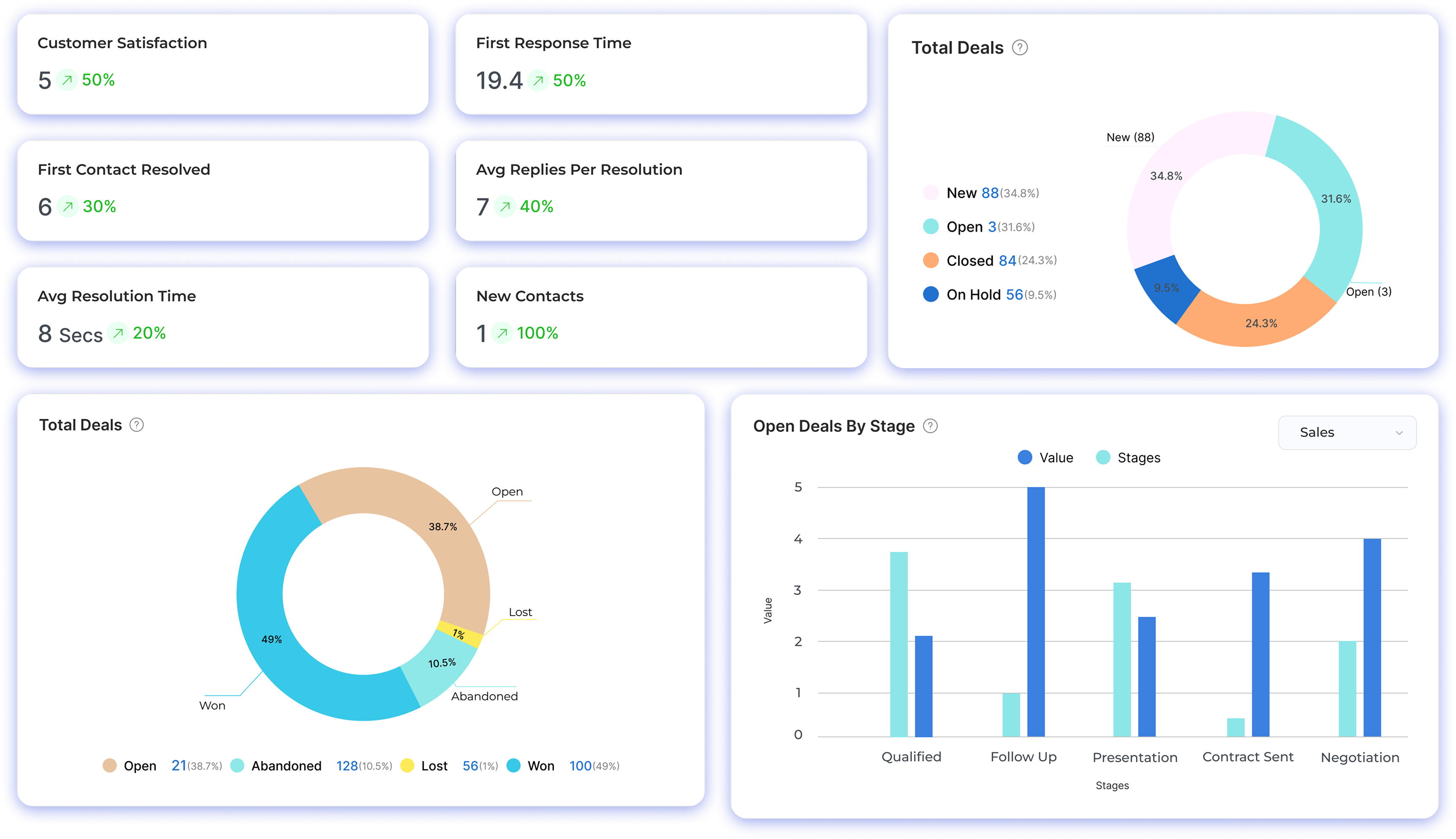
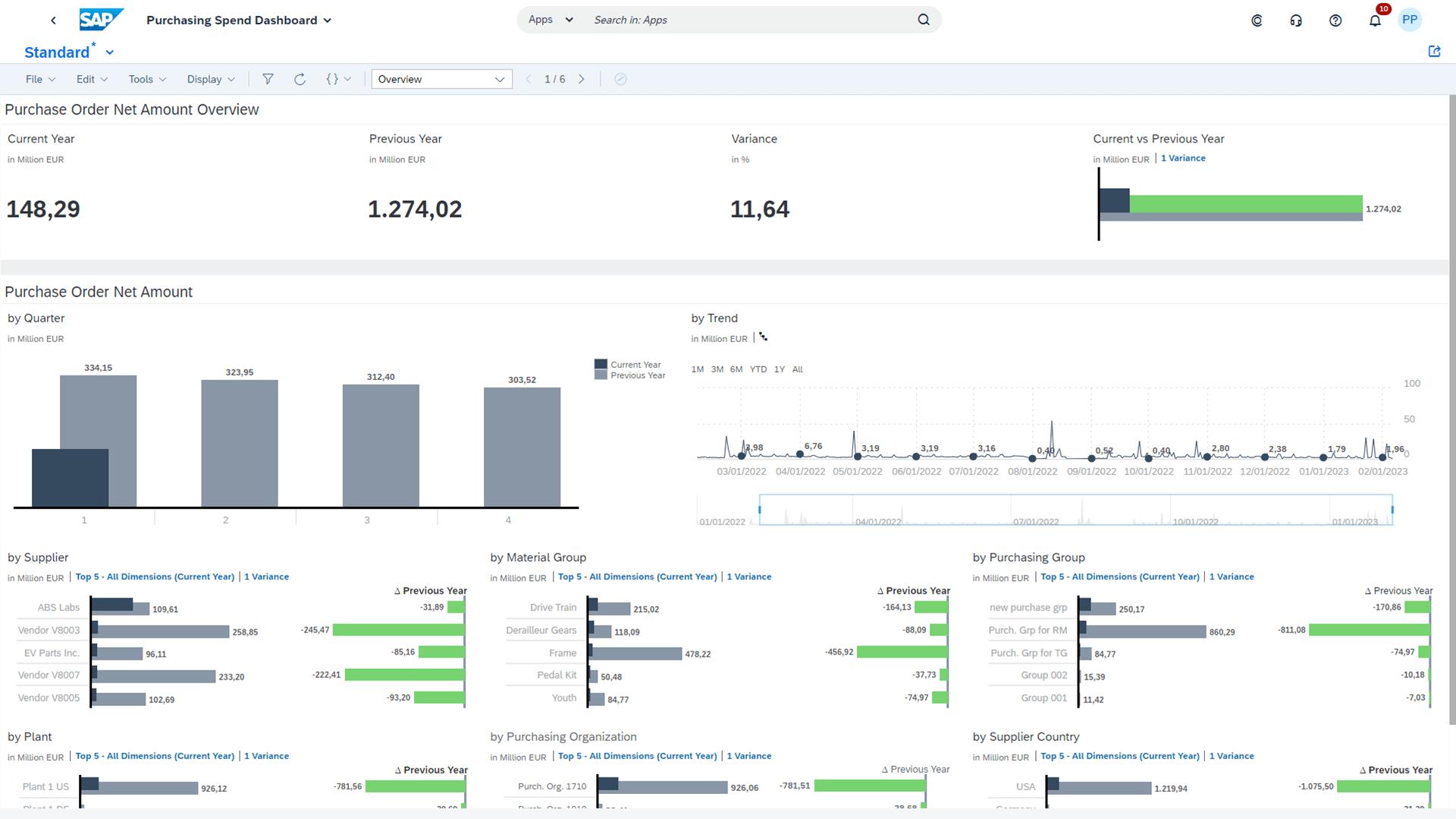
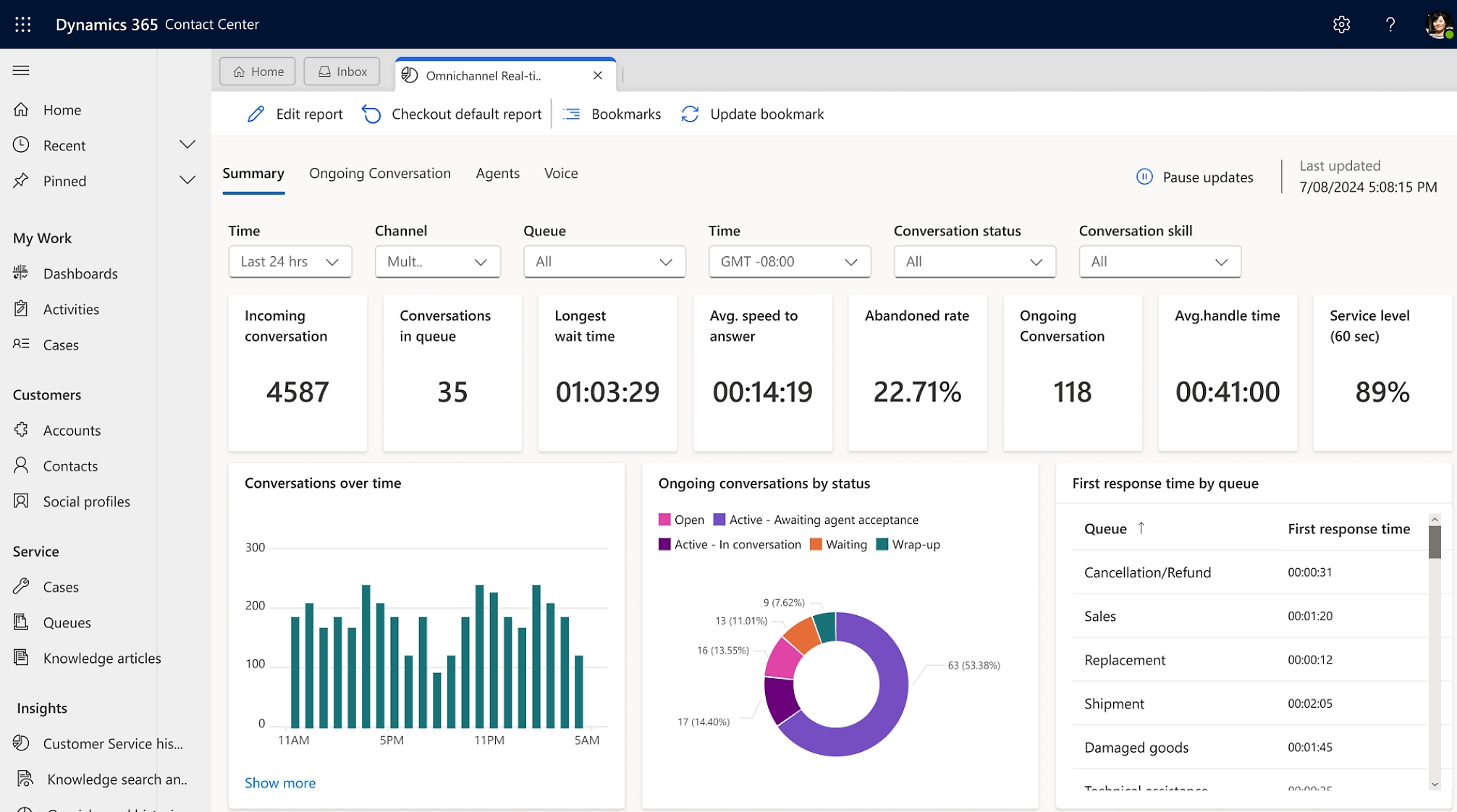
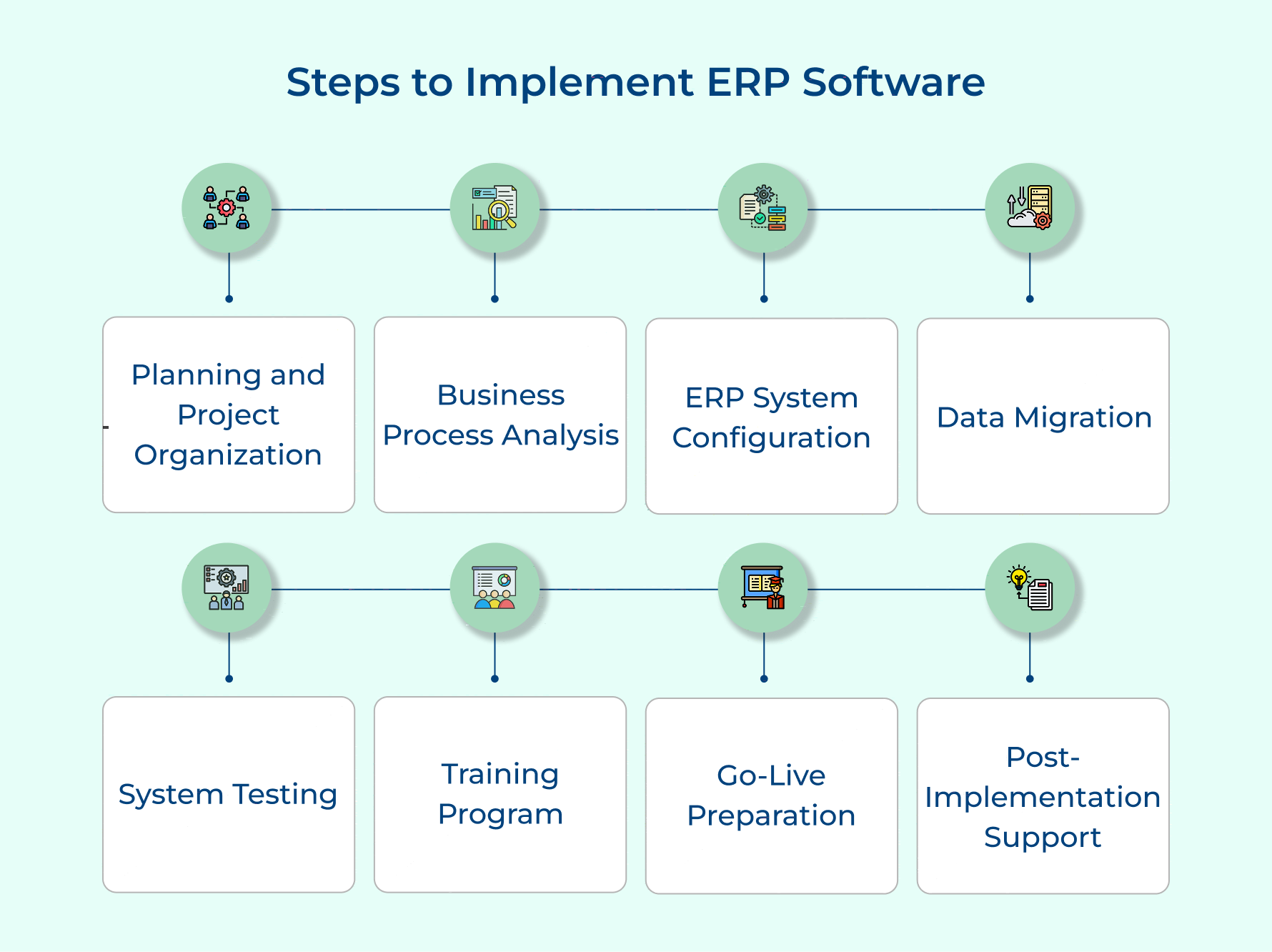
Step 1: Planning and Project Organization
Start by forming a team, setting clear goals, and assigning resources. Good planning avoids delays and keeps the project on track. Make a detailed plan with tasks, deadlines, and roles. Use tools to track progress and hold regular check-ins.
Actionable tips:
- Create a RACI matrix (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) for all stakeholders and update it monthly to maintain clear ownership of tasks.
- Schedule bi-weekly steering committee meetings with fixed agendas to ensure continuous executive support and quick decision-making.
Step 2: Business Process Analysis
Review your current processes to see what works and what needs improvement. This helps you avoid copying bad habits into the new system. Talk to employees, map out workflows, and design improved processes using ERP features.
Tips to consider:
- Use process mining tools to automatically discover and analyze current workflows, saving time and ensuring accuracy.
- Create a process improvement registry to track and prioritize optimization opportunities identified during analysis.
Step 3: ERP System Configuration
Customize the ERP system to fit your business needs. This includes setting up modules, workflows, and user roles. Test configurations in a sandbox environment before applying to production. Document all configuration decisions and rationales.
actionable tips:
- Create a configuration workbook that tracks all settings, parameters, and decision rationales for future reference.
- Implement a change control process for configuration modifications to maintain system integrity.
Step 4: Data Migration
Data migration involves transferring information from old systems to the new ERP, ensuring it’s clean, accurate, and properly mapped. It preserves historical data and maintains consistency across business functions.
A strong strategy includes data cleaning, automation, validation, and multiple test runs to ensure smooth, error-free integration into the ERP system.
Pro tips:
- Create a data quality scorecard to measure and track the accuracy of migrated data against defined criteria.
- Perform incremental data migrations instead of one big bang approach to manage risks effectively.
Step 5: System Testing
System testing ensures the ERP works correctly, meets business needs, and integrates with other tools. It helps catch issues early and confirms the system can handle real use. Create detailed test cases, involve users in testing, and track all issues to make sure everything runs smoothly before go-live.
Actionable tips:
- Use automated testing tools for regression testing to save time and ensure consistency.
- Create a defect triage process with clear severity levels and resolution timeframes.
Step 6: Training Program
ERP training prepares users to confidently use the system through role-based guides, hands-on practice, and support resources. Effective training boosts user adoption, reduces errors, and improves productivity.
Offer tailored sessions, provide helpful materials, and track user progress to ensure everyone is ready for a smooth transition.
Tips to consider:
- Create short video tutorials for common tasks that users can reference after training.
- Implement a train-the-trainer program to build internal expertise and support capacity.
Step 7: Go-Live Preparation
Go-live preparation is the last step before launching the ERP system. It includes final data migration, cutover planning, and team coordination to ensure a smooth rollout. A solid plan reduces disruption, keeps everything on track, and ensures support is ready to handle any issues during the transition.
Pro tips:
- Create a detailed hour-by-hour cutover schedule with clear go/no-go decision points.
- Establish a command center during go-live with representatives from all key areas.
Step 8: Post-Implementation Support
Post-implementation support keeps the ERP system running smoothly after launch. It includes fixing issues, improving features, and helping users as they adapt. Regular monitoring, feedback collection, and system updates ensure the ERP continues to meet business needs as well as supports ongoing growth.
Actionable tips:
- Implement a user feedback system to continuously collect improvement suggestions and prioritize enhancements.
- Create monthly system health reports tracking key metrics like performance, usage, and issue trends.