Project Monitoring and Control: Planning & Techniques
- What is Project Monitoring and Controlling?
- Why is Project Monitoring and Controlling Important?
- How to Create a Project Monitoring and Control Plan?
- Project Monitor and Control Techniques
- Key Challenges in Project Monitoring and Control
- Achieve Excellence with Project Monitoring and Controlling
- FAQs about Project Monitoring and Control

Key Highlights:
- Project monitoring and control ensure alignment with goals, and prevent scope creep while keeping budgets on track through regular progress tracking.
- Using KPIs, dashboards, and structured reviews helps agencies make data-driven decisions as well as enhance team collaboration.
- Risk management processes ensure project stability, mitigate issues early, and maintain stakeholder trust.
Project managers are juggling more complexity than ever. With limited visibility into project health, resource use, and risks, it’s easy for things to slip through the cracks.
Without proper monitoring systems, organizations find themselves scrambling to solve problems after they’ve already spiraled. But the good news is—effective monitoring frameworks provide clarity and early warnings, empowering teams to make data-driven decisions as well as act fast.
Let’s dive into the project monitoring and control strategies that will transform how you manage your projects for consistent success.
What is Project Monitoring and Controlling?
Project control and monitoring represents a continuous process of tracking, reviewing, as well as regulating project progress. It involves systematically observing project execution to identify variations from the project management plan, analyzing potential problems, and implementing corrective measures.
Monitoring and controlling mechanisms ensure accountability as well as maintain quality standards, while providing stakeholders with accurate project status information. A robust monitoring system helps maintain project momentum while enabling informed decision-making based on actual performance data.
Key objectives:
- Performance tracking: Measure actual progress against planned milestones and deliverables to ensure alignment with project objectives.
- Risk management: Identify potential issues early and implement mitigation strategies to minimize impact on project success.
- Resource optimization: Monitor resource allocation and utilization to maximize efficiency as well as prevent overallocation or underutilization.
- Quality assurance: Ensure deliverables meet established standards and specifications through regular reviews/assessments.
Why is Project Monitoring and Controlling Important?
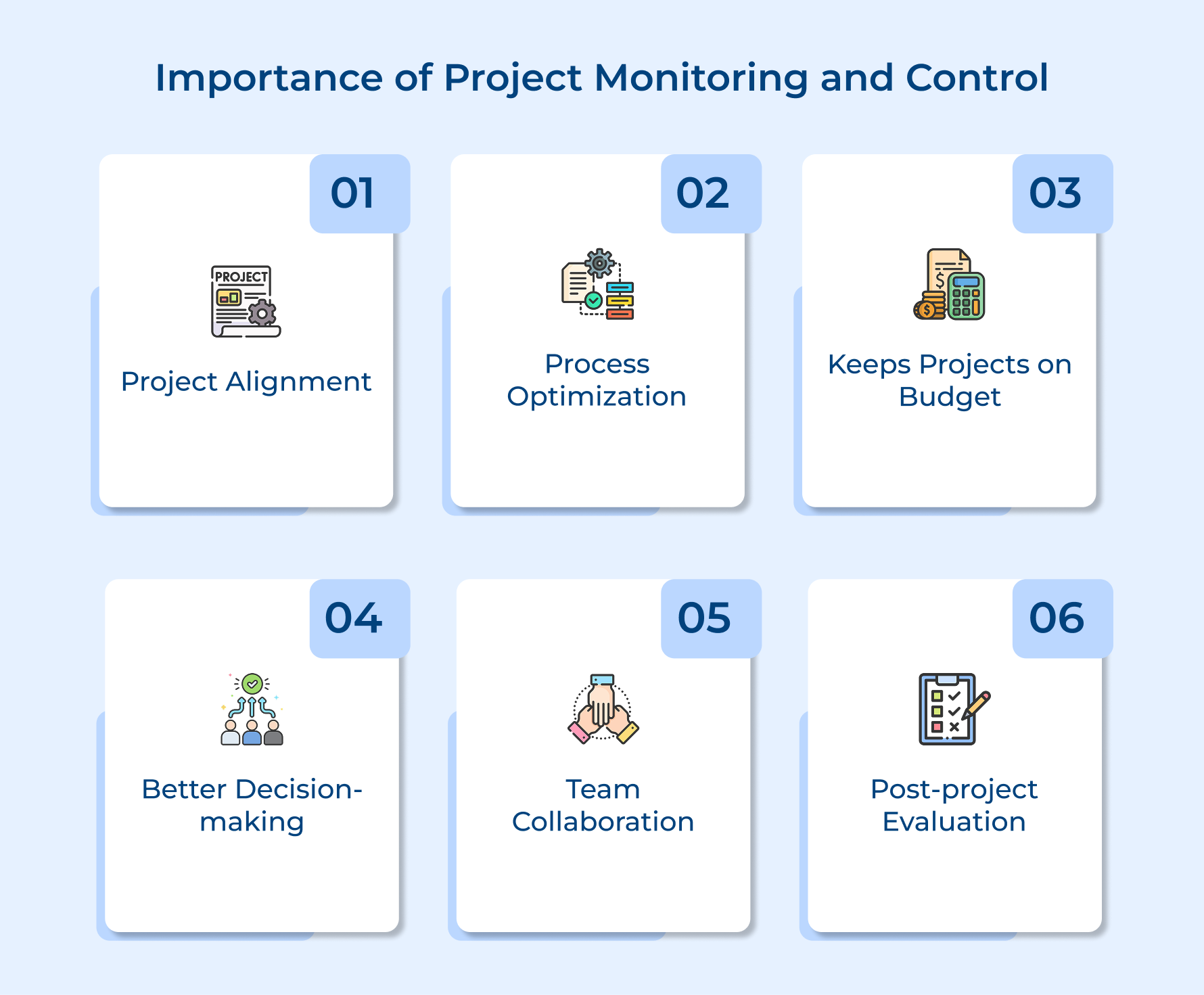
Project monitoring and controlling are key to ensuring projects stay on track. They help track progress, identify risks early, and keep everything aligned with goals. Let’s explore its importance.
Ensures Project Alignment with Client Expectations
Effective monitoring helps agencies stay aligned with client goals and expectations. Regular progress checks prevent scope creep, ensuring projects meet deadlines and deliver quality.
Process Optimization
Monitoring uncovers inefficiencies and bottlenecks in workflows. Agencies can streamline processes while also improving service delivery based on insights and performance data.
Keeps Projects on Budget
Continuous tracking of expenses and resources ensures agencies stay within budget. Early detection of overspending allows for quick corrective action to prevent financial strain.
Promotes Better Decision-Making
With real-time data, agencies can adjust strategies, reassign resources, or shift timelines. Accurate insights help make better decisions and improve project outcomes.
Strengthens Team Collaboration
Monitoring task progress fosters communication among team members. Identifying areas for support helps improve collaboration and enhances team performance.
Facilitates Post-Project Evaluation
Project monitoring provides valuable data for post-project reviews. Agencies can reflect on performance, learn from experiences, and apply those lessons for future improvements.
How to Create a Project Monitoring and Control Plan?
Let’s dive into creating the steps in project monitoring and control for building an effective plan that ensures success.
1. Define Project Objectives and Scope
Setting clear project objectives ensures everyone knows what needs to be achieved and what’s outside the project’s scope. Here’s how to define and monitor objectives effectively:
- Set clear goals & deliverables – Clearly outline what the project aims to achieve and what success looks like.
- Use SMART criteria – Make objectives Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound for better tracking.
- Establish monitoring checkpoints – Regularly review progress to ensure the project stays on track.
- Prevent scope creep – Stick to defined boundaries to avoid unnecessary changes that could derail the project.
Tips to consider:
- Create a scope statement matrix with clear inclusion/exclusion criteria and get stakeholder sign-off.
- Develop a project charter template that captures objectives, deliverables, and monitoring milestones.
2. Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs help measure project success by tracking key aspects like time, cost, quality, and resources. They ensure you stay on top of performance as well as spot issues early.
- Track Key Metrics – Monitor time, budget, quality, and team productivity to measure progress.
- Use Real-Time Dashboards – Keep KPIs visible to make quick, informed decisions.
- Regular Reporting – Review performance data frequently and adjust strategies as needed.
- Identify & Fix Issues Early – Use KPIs to catch potential problems before they impact the project.
Actionable tips:
- Select 5-7 core KPIs that directly align with project objectives and stakeholder expectations.
- Create automated tracking systems with clear thresholds for triggering alerts or interventions.
3. Establish Monitoring Methods and Tools
Monitoring methods and tools are systematic ways to track how a project is progressing, collect data, as well as measure performance against your plans.
When you use consistent monitoring methods, you ensure that the data you collect is reliable and your analysis is on point. The right tools make the process smoother and give you accurate, timely information to make decisions.
To implement this, start by using project management software for tracking. Then, create standardized templates as well as processes for data collection and reporting. It helps keep everything consistent and clear across the project.
Pro tips:
- Select integrated tools that automate data collection and provide real-time visibility.
- Develop standardized monitoring templates and train team members on their use.
4. Define Roles and Responsibilities for Monitoring
Clear assignment of monitoring duties and accountability for different aspects of project control. Establishes who collects data, analyzes results, and takes action on findings.
Role clarity prevents monitoring gaps and ensures comprehensive coverage. It establishes accountability as well as ensures someone is responsible for each monitoring aspect.
Create RACI matrices for monitoring activities. Establish clear reporting lines and escalation paths for identified issues or concerns.
Tips to consider:
- Create detailed role descriptions with specific monitoring responsibilities and frequencies.
- Implement a backup system ensuring coverage during team member absences.
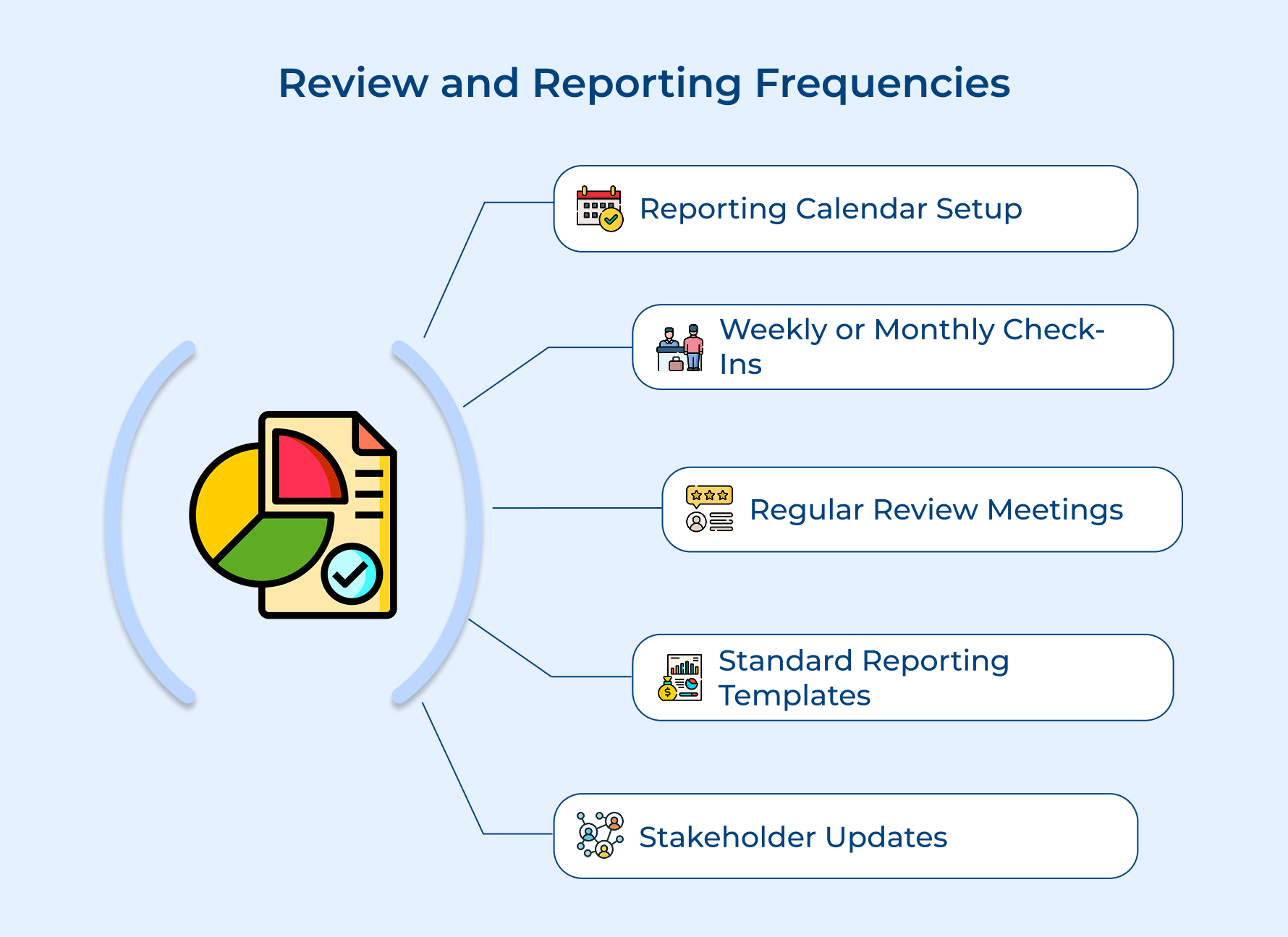
5. Set Review and Reporting Frequencies
It’s about defining when and how often you’ll check in on different parts of the project. This helps you stay on top of things and catch issues or opportunities early.
Here’s why they’re important,
- Regular reviews help you spot problems or opportunities quickly.
- Consistent reporting keeps stakeholders in the loop and ensures everyone has a clear picture of how the project is going.
How can you make this happen?
- Create a reporting calendar that outlines how often different metrics need to be checked (e.g., weekly, monthly).
- Schedule regular review meetings to discuss progress.
- Use standard reporting templates to keep things clear and consistent.
Actionable tips:
- Create a master calendar showing all review and reporting deadlines.
- Develop automated report generation systems to ensure timely delivery.
6. Create a Risk Management Plan
A systematic approach to managing project risks involves identifying, assessing, and responding to potential issues. It includes using tools like risk registers, planning mitigation strategies, and setting up monitoring procedures to keep track of risks.
Being proactive can help you prevent risks from derailing your project and ensure stability when uncertainties arise. Keep an updated risk register and review it regularly.
Use metrics to track risks and have clear protocols in place to respond to risks based on their severity. The structured approach helps you stay prepared and keeps your project on track.
Tips to consider:
- Create a risk assessment matrix with clear triggers for different response levels.
- Schedule bi-weekly risk review sessions with key stakeholders to assess new and existing risks.
7. Establish Change Control Procedures
Formal processes for handling project changes involve evaluating, approving, and implementing them in a structured way. It assesses the impact of changes and documents all change requests properly.
Change control helps keep the project on track by preventing unauthorized adjustments and making sure any changes are carefully reviewed before they’re put into action.
Set up a system for submitting and approving change requests with clear workflows. Also, keep track of how changes affect the project’s timeline, budget, and resources to avoid any surprises.
Pro tips:
- Develop a change request form template with clear impact assessment sections.
- Create a change control board with defined authority levels for different types of changes.
8. Set Up Corrective Action Procedures
They’ve defined processes for tackling issues or deviations from your project plans. Think of them as your game plan for fixing problems, complete with escalation steps and ways to track progress. Corrective action procedures are crucial because,
- They help you respond quickly and effectively when things go off track.
- They give you a clear structure to solve problems and stop them from happening again.
How to make it work?
- Set up issue logs to track problems and their status.
- Define clear timeframes for responding to issues.
- Add a step to verify that issues are fully resolved—no loose ends!
Best tips:
- Implement an issue-tracking system with priority levels and response timelines.
- Create standard operating procedures for common project issues and their resolution.
9. Monitor Quality Control Measures
Quality assurance is all about making sure your deliverables meet the required standards. It includes setting clear quality metrics, review procedures, and acceptance criteria to maintain consistency.
You can avoid issues that could impact project success or client satisfaction by actively monitoring quality.
Implement quality checkpoints at key stages, use detailed review checklists, and follow verification procedures to catch any problems early.
Tips to consider:
- Develop detailed quality checklists for each major deliverable type.
- Establish peer review processes with standardized feedback forms.
10. Document and Analyze Performance Data
Tracking project performance means collecting while also analyzing key metrics to see what’s working and what needs improvement.
Regular performance tracking helps teams make informed decisions and optimize processes for future projects.
Set up dashboards and trend reports to visualize progress, spot patterns, as well as adjust strategies as needed.
Best tips:
- Implement a centralized data repository with clear organization and access controls.
- Schedule monthly performance analysis sessions to identify trends and improvement opportunities.
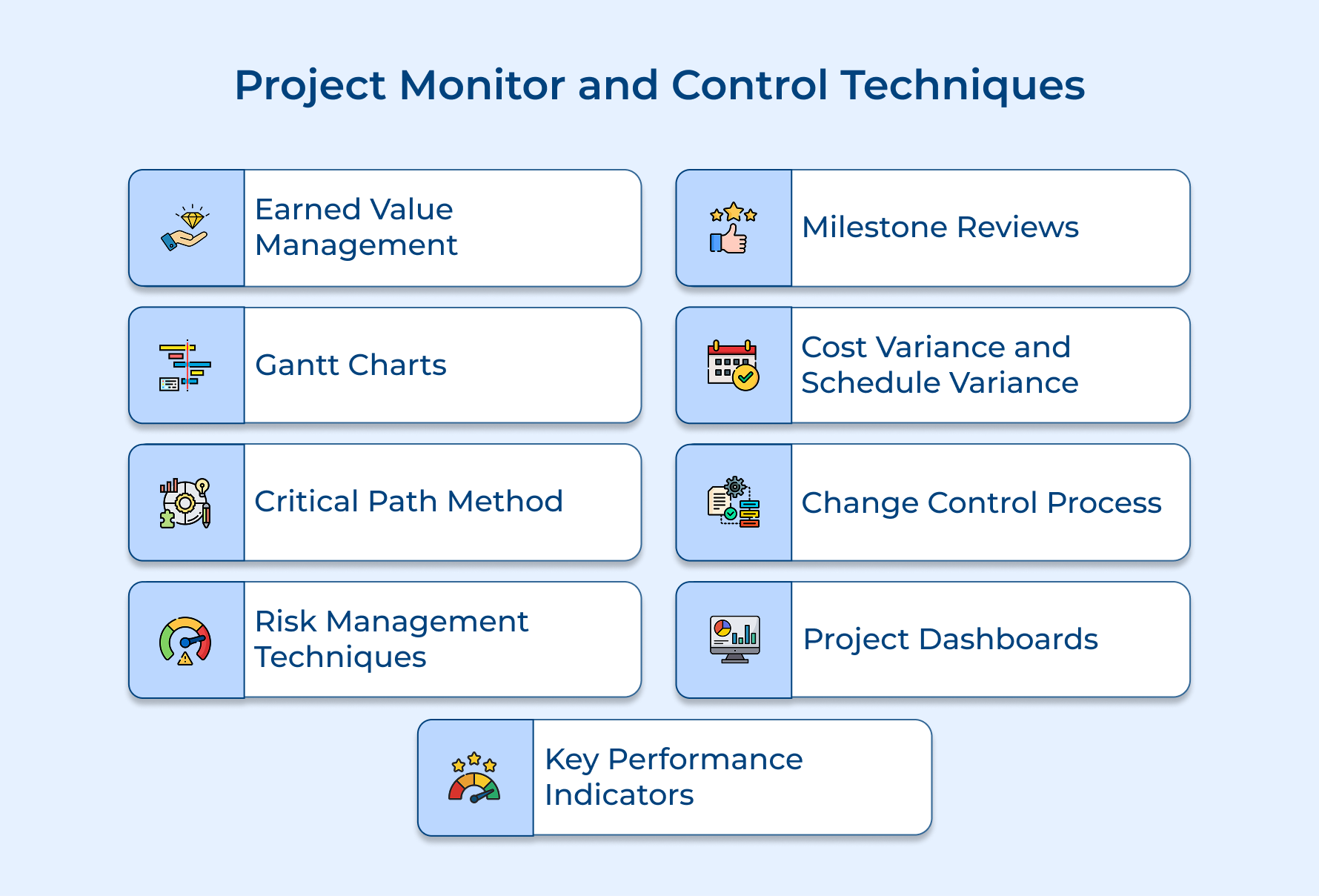
Project Monitor and Control Techniques
Effective project monitoring and control techniques help teams stay on track, manage risks, as well as ensure quality. Let’s explore key methods to keep projects running smoothly.
1. Earned Value Management (EVM)
Earned Value Management is a technique used to assess a project’s performance by comparing the planned progress with the actual work completed. It integrates project scope, schedule, and cost to provide a comprehensive view of project health.
EVM uses key metrics:
- Planned Value (PV): The budgeted cost for work scheduled.
- Earned Value (EV): The budgeted cost for work performed.
- Actual Cost (AC): The actual cost incurred for the work performed.
Why it’s useful:
EVM helps project managers determine if the project is ahead, on schedule, or behind and whether costs are under or over budget. It allows for timely corrective actions.
2. Gantt Charts
A Gantt chart is a visual timeline used to plan and monitor project schedules. It represents tasks as well as their durations along a horizontal timeline.
How it works:
Tasks are listed on the vertical axis, with time intervals on the horizontal axis. Each task is represented by a bar, and dependencies between tasks are shown by connecting lines.
Why it’s useful:
Gantt charts help track project progress visually, identify delays, and monitor dependencies. They are especially useful for keeping the team aligned while ensuring milestones are met on time.
3. Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method is used to determine the longest sequence of dependent tasks and the minimum project duration. It identifies the tasks that directly impact the project completion date.
How it works:
Tasks are broken down into a network diagram, and the critical path is identified by calculating the longest path through the project. Any delay in a task on the critical path will delay the entire project.
Why it’s useful:
CPM helps prioritize tasks that are crucial to the project’s timely completion. It highlights where to focus resources and attention to avoid delays.
4. Risk Management Techniques
Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and controlling risks that could potentially impact a project. Monitoring risks throughout the project allows for early detection and mitigation.
How it works:
Risks are identified in the planning phase, followed by a risk analysis (qualitative or quantitative). Mitigation strategies are developed, and risks are monitored regularly throughout the project.
Why it’s useful:
Proactive risk management ensures that potential issues are identified early, reducing the likelihood of project delays or cost overruns. Techniques like risk registers, Monte Carlo simulations, and sensitivity analysis are commonly used.
5. Milestone Reviews
Milestone reviews are checkpoints where project progress is assessed against predetermined milestones or phases. The reviews evaluate if the project is on track to meet key goals.
How it works:
At each milestone, project deliverables and progress are reviewed, while performance is compared against the project plan. Any deviations or issues are addressed immediately.
Why it’s useful:
Milestone reviews provide an opportunity to ensure the project is progressing as planned and to make course corrections if necessary. They also help maintain stakeholder engagement and trust by demonstrating progress.
6. Cost Variance (CV) and Schedule Variance (SV)
Cost variance and schedule variance are financial as well as time-based metrics used to assess a project’s performance. They help monitor if the project is on budget and schedule.
How it works:
- Cost Variance (CV): The difference between Earned Value (EV) and Actual Cost (AC). A positive CV means the project is under budget.
- Schedule Variance (SV): The difference between Earned Value (EV) and Planned Value (PV). A positive SV means the project is ahead of schedule.
Why it’s useful:
CV and SV provide a quick snapshot of the project’s performance, allowing managers to make timely adjustments to the budget or schedule to keep the project on track.
7. Change Control Process
The change control process ensures that any changes to the project scope or budget are properly documented and approved before being implemented.
How it works:
Changes are requested through formal change requests, which are then assessed by a change control board (CCB). If the change is deemed necessary and feasible, it is approved as well as integrated into the project plan.
Why it’s useful:
A structured change control process helps prevent scope creep and ensures that all changes are carefully considered, minimizing their impact on project timelines as well as cost.
8. Project Dashboards
Project dashboards provide a real-time, visual representation of a project’s key metrics, such as budget, schedule, risk status, and progress toward goals.
How it works:
Dashboards aggregate data from project management tools, such as Gantt charts or EVM, and present it in a visually digestible format. It includes graphs, charts, and color-coded indicators to highlight issues or successes.
Why it’s useful:
Dashboards allow project managers to quickly assess the health of a project and make data-driven decisions. They are valuable for high-level oversight and can be shared with stakeholders for transparency.
9. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs are measurable values that help monitor the performance and success of a project. These can be related to scope, time, cost, or quality.
How it works:
KPIs are defined at the start of the project and tracked throughout its lifecycle. Common project KPIs include cost performance index (CPI), schedule performance index (SPI), customer satisfaction, and deliverable quality.
Why it’s useful:
KPIs provide concrete metrics that help evaluate progress and success. They allow project managers to make adjustments if performance falls short of expectations.
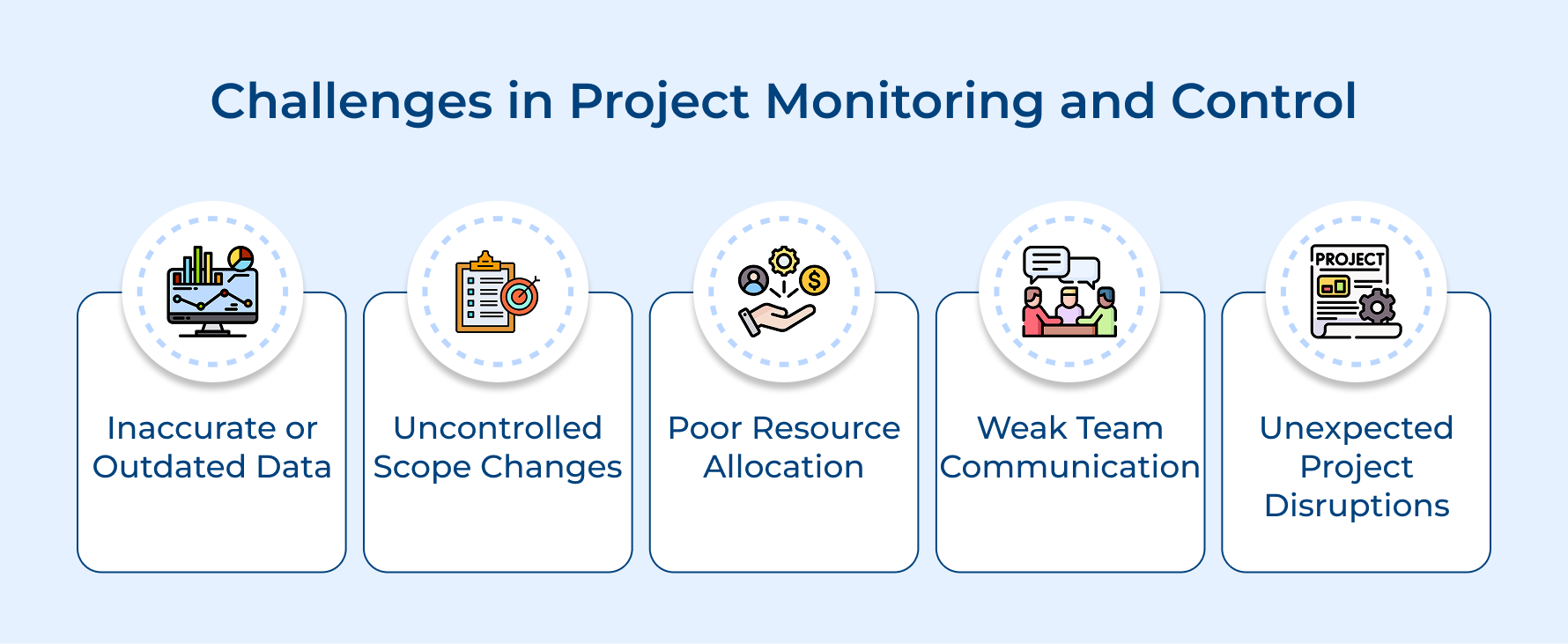
Key Challenges in Project Monitoring and Control
Project monitoring and control come with challenges like scope creep, resource constraints, as well as data accuracy issues. Let’s explore common hurdles and how to tackle them.
1. Lack of Accurate Data
Accurate and up-to-date data is essential for effective project monitoring. Without it, decisions are based on assumptions, leading to errors and delays.
Implement reliable tracking systems and tools to collect real-time data. Ensure teams update progress regularly and use automated reporting tools to reduce human error. Standardize data formats and ensure all stakeholders have access to accurate project information.
2. Scope Creep
Scope creep occurs when the project’s objectives, deliverables, or timeline expand without proper control. This can lead to missed deadlines and budget overruns.
Establish a clear project scope from the outset and use a formal change management process. Regularly review project goals and deliverables with stakeholders to ensure any changes are documented, evaluated, as well as approved before being implemented.
3. Inadequate Resource Allocation
Poor resource management can result in overburdened teams or underutilized resources, impacting productivity and project timelines.
Use resource management tools to track and allocate resources based on project needs. Plan for peak workload times, and ensure resources are distributed equitably. Reassess resource allocation regularly to make adjustments as the project progresses.
4. Ineffective Communication
Miscommunication or a lack of communication can cause confusion, delays, and missed opportunities to address issues early.
Establish clear communication protocols and tools for regular status updates. Schedule frequent team meetings to discuss progress, challenges, and risks. Use collaboration platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams to keep all team members and stakeholders informed.
5. Unforeseen Risks and Issues
Unexpected risks, such as technical problems or resource shortages, can derail progress and affect project outcomes.
Fix: Conduct thorough risk assessments during the planning phase and develop a risk management plan. Identify potential risks early and establish mitigation strategies. Regularly revisit the risk register throughout the project to adjust for new risks and issues.
Achieve Excellence with Project Monitoring and Controlling
Project monitoring and controlling transform vision into reality through systematic oversight along with timely adjustments. Well-implemented monitoring systems serve as early warning mechanisms, preventing minor issues from becoming major roadblocks.
Success demands commitment to regular monitoring, clear communication channels, and decisive action when needed. Teams embracing robust monitoring practices consistently outperform those relying on reactive management approaches.
Moving forward, focus on building monitoring habits that enhance rather than hinder project flow. Every improvement in monitoring effectiveness compounds into significant project benefits.
Limit time — not creativity
Everything you need for customer support, marketing & sales.
Neeti Singh is a passionate content writer at Kooper, where he transforms complex concepts into clear, engaging and actionable content. With a keen eye for detail and a love for technology, Tushar Joshi crafts blog posts, guides and articles that help readers navigate the fast-evolving world of software solutions.