Project Cost Estimation Process & Best Practices for Managers
- What is Project Cost Estimation?
- Why is Estimating Project Costs Necessary?
- What are Project Cost Estimation Methods?
- 7 Strategic Project Cost Estimation Steps for Better Control
- How to Utilize Agency Management Software for Project Cost Estimation?
- Best Practices for Cost Estimation in Project Management
- Strengthening Profitability with Smart Project Cost Estimation
- FAQs about Project Cost Estimation

Key Highlights
When it comes to project management, every agency should be cautious about multiple things like resources, utilization, and labor costs. However, the most important of them all is the project cost estimation. It’s not just about knowing how much a project will cost, but about planning for both the obvious expenses and those sneaky overheads that often get overlooked.
Getting the numbers right from the start helps set the stage for everything—whether it’s budgeting, resource allocation, or even deciding if the project is worth pursuing in the first place. Plus, clear cost estimates mean you can manage client expectations, avoid surprises, and stay profitable.
Let’s explore each aspect of project cost estimation ensuring that your agency is equipped to handle the project smoothly while keeping expenses in check.
What is Project Cost Estimation?
Project cost estimation is the process of forecasting the financial resources required to complete a project within a defined scope and timeline. It involves quantifying all expenses associated with project activities that include labor, materials, services and potential risks.
Precise cost estimates contribute to competitive pricing strategies, allowing agencies to win bids while maintaining profit margins. They also play a crucial role in risk management by helping to identify and quantify potential financial risks, enabling the allocation of appropriate contingencies.
Primary objectives:
- Determine project feasibility and inform go/no-go decisions based on projected costs as well as potential returns.
- Establish a realistic budget baseline for effective financial planning and control throughout the project lifecycle.
- Support accurate pricing and proposal development to win clients while ensuring project profitability.
- Facilitate informed decision-making regarding resource allocation, risk management, and project execution strategies.
Why is Estimating Project Costs Necessary?
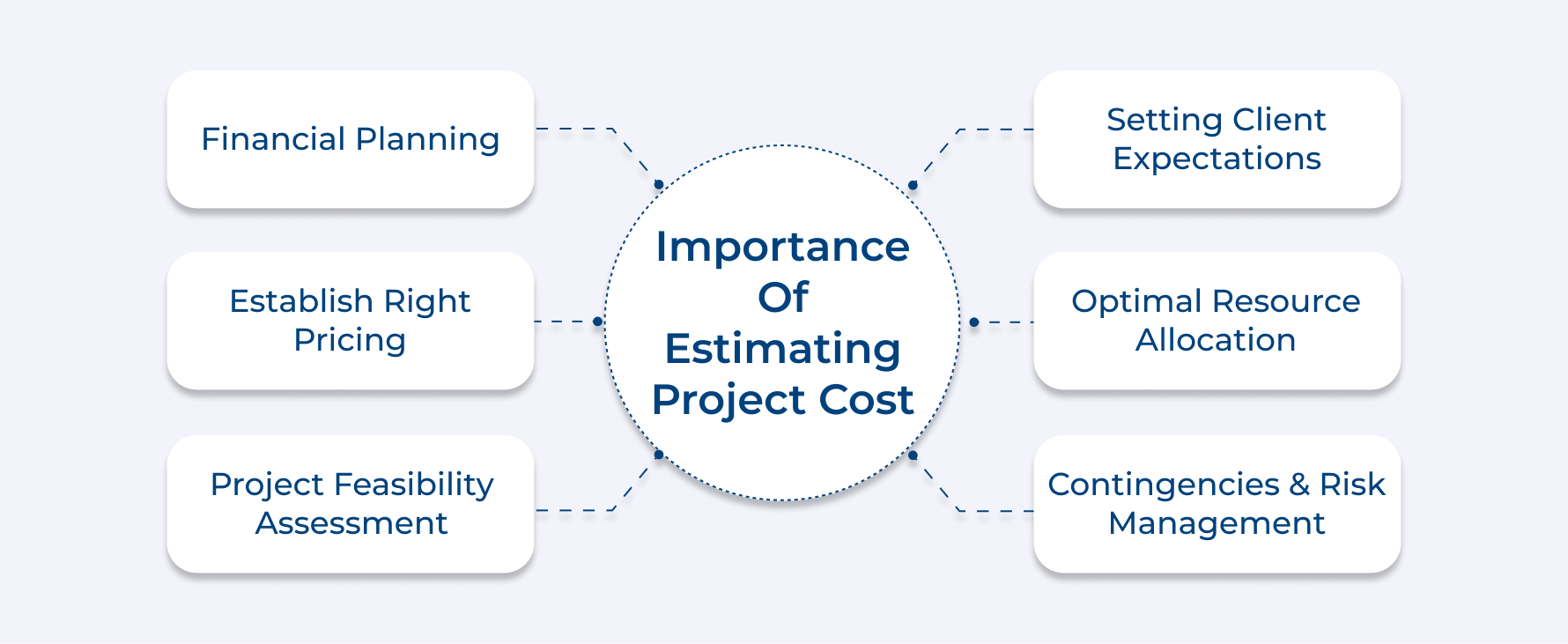
The core agenda for the estimation is to avoid any kind of cost overruns, which often surface due to common agency project management challenges after the project moves forward. Here’s the list of other reasons why it is important.
1. Financial planning and budgeting: Accurate cost estimation provides a clear picture of expected expenses, enabling proper budgeting and cash flow management. Foresight helps agencies allocate resources efficiently and maintain financial stability.
2. Establish right pricing: Accurate cost estimates form the basis for pricing strategies. It enables agencies to set competitive yet profitable rates for their services, balancing the need to win clients with the imperative to maintain healthy profit margins.
3. Project feasibility assessment: By estimating costs upfront, agencies can evaluate if a project is financially viable. The assessment helps in making informed decisions about which projects to pursue, avoiding those that may lead to financial losses.
4. Setting client expectations: Detailed cost estimates allow agencies to set realistic expectations with clients regarding project scope, timeline, and deliverables. The transparency helps build trust and reduces the likelihood of disputes over costs later in the project.
5. Optimal resource allocation: You get to gather insights into the resources required for a project, including personnel, equipment, and materials. It becomes crucial for effective resource planning and allocation across multiple projects.
6. Contingencies & risk management: The process of cost estimation often reveals potential financial risks associated with a project. The awareness allows agencies to develop contingency plans and allocate appropriate reserves, mitigating the impact of unexpected expenses or challenges.
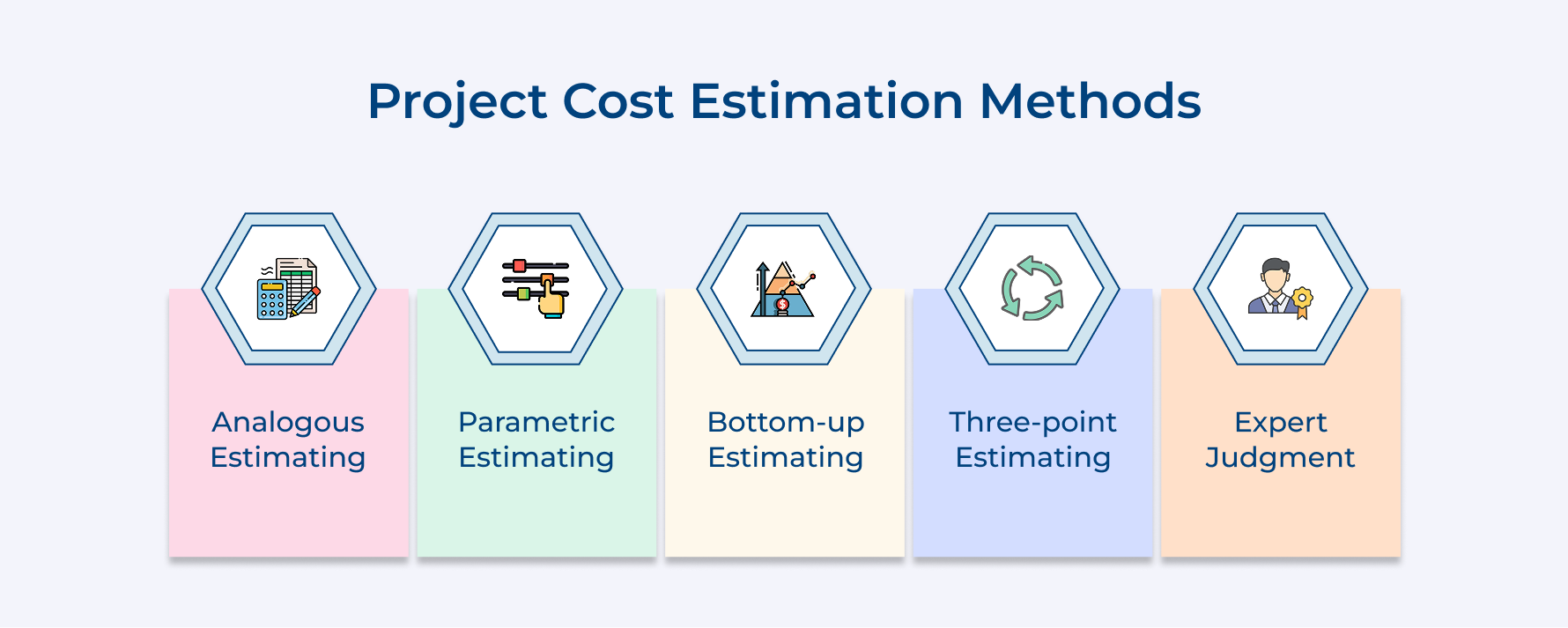
What are Project Cost Estimation Methods?
Each method has its strengths and is suited to different project types. Often, a combination of methods is used to arrive at the most reliable cost estimate, let’s delve into them.
1. Analogous Estimating
The analogous method uses historical data from similar projects to estimate costs for the current project. It’s particularly useful when detailed information about the new project is limited.
Analogous estimating is quick and relatively easy but may lack accuracy if projects aren’t truly comparable. It’s best used in early project stages or for high-level estimates. To improve accuracy, adjust for known differences between the past and current projects.
For instance: An agency is estimating the cost of a new website development project. They look at a similar website project completed last year, which cost $50,000. Considering some additional features in the new project, they estimate the cost at $60,000.
2. Parametric Estimating
Parametric estimating uses statistical relationships between historical data and other variables to calculate cost estimates. For example, if you know the average cost per square foot for office renovation, you can estimate a new renovation project’s cost based on its square footage.
The method can be more accurate than analogous estimating but requires reliable data to establish valid cost relationships. It’s particularly useful for projects with quantifiable parameters.
For example: A marketing agency knows from past campaigns that social media ad spending typically costs $0.50 per click. For a new campaign targeting 100,000 clicks, they estimate the ad spend at $50,000 using this parametric model.
3. Bottom-up Estimating
The given approach involves estimating costs for individual work packages or activities and then summing these up to determine the overall project cost. Bottom-up estimating is often the most accurate method but also the most time-consuming.
It’s best used when detailed project information is available and high accuracy is required. The bottom-up method also helps in creating a more detailed project budget and schedule.
For Instance: For a branding project, the agency breaks down tasks: logo design (40 hours), brand guidelines (30 hours), and brand assets (20 hours). They multiply each by the hourly rate and sum up the total project cost.
4. Three-point Estimating
Project estimates can be determined using three scenarios – optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic – to create a range of potential costs. The final estimate is a weighted average of these three points.
Three-point estimating accounts for uncertainty and provides a more realistic range of potential costs. It’s particularly useful for projects with significant unknowns or risks.
For Instance: For a video production project, the agency estimates costs as: Optimistic ($15,000), Most Likely ($20,000), Pessimistic ($30,000). Using the formula (O + 4M + P) / 6, they calculate an expected cost of $20,833.
5. Expert Judgment
The expert judgment method relies on the knowledge and experience of subject matter experts to estimate costs. It’s often used in conjunction with other methods or when historical data is lacking.
The method can be valuable for unique or specialized projects but may be subjective. To improve accuracy, consult multiple experts and use techniques like the Delphi method to reach a consensus.
Example: For a new AR (Augmented Reality) app development project, the agency consults with their most experienced AR developer to estimate the time and resources required, as they lack historical data for this type of project.
7 Strategic Project Cost Estimation Steps for Better Control
Project cost estimation requires a proper understanding of individual tasks, direct costs, and overhead costs related to it. The below steps should be able to complete the task effortlessly.
1. Define Project Scope and Objectives
Project cost estimation depends heavily on a well-structured project scope in project management and clearly stated objectives. It provides a clear understanding of what the project entails, its boundaries, and expected outcomes. Without this clarity, cost estimates may be inaccurate or incomplete, leading to budget overruns.
Use the defined scope and objectives as a foundation for all subsequent cost estimation steps. Refer to this definition when identifying tasks, resources, and potential risks to ensure all cost elements are aligned with the project’s goals.
Tips to consider:
- Conduct a thorough stakeholder analysis to ensure all perspectives are considered in defining the project scope and objectives.
- Create a detailed scope statement that clearly outlines what is and isn’t included in the project, reducing the risk of scope creep as well as unexpected costs.
2. Break Down the Project into Tasks
Breaking the project into smaller, manageable tasks provides a granular view of the work required. This detailed breakdown allows for more accurate cost estimation at each level and helps identify potential areas of cost uncertainty.
Leverage the task breakdown to create a comprehensive Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). The WBS then becomes the framework for estimating costs associated with each task, resource allocation, and schedule development.
Tips to consider:
- Involve team members with relevant expertise in creating the WBS to ensure all necessary tasks are identified and properly categorized.
- Use a numbering system in your WBS to create a clear hierarchy of tasks and subtasks, facilitating easier cost rollup as well as tracking.
3. Estimate Resource Requirements
Estimating resource requirements is essential for understanding the full scope of project costs. It helps identify all necessary inputs from personnel to equipment and materials ensuring no cost elements are overlooked.
Resource estimates help you determine the quantity and type of resources needed for each task. The information guides cost calculations and helps in creating a resource management plan to ensure availability when needed.
Tips to consider:
- Create a detailed resource breakdown structure (RBS) that categorizes all types of resources required for the project.
- Consult with subject matter experts and review historical data from similar projects to validate your resource estimates.
4. Apply Cost Estimation Techniques
Applying appropriate cost estimation techniques ensures that your estimates are as accurate as possible. Different methods suit different scenarios, and using the right technique can significantly improve the reliability of your cost projections.
A combination of estimation techniques such as analogous, parametric, or bottom-up estimating helps calculate costs for each project component, while useful project management tricks for planning support better method selection. Apply the most suitable method based on available data and the nature of each task.
Tips to consider:
- Maintain a database of historical project data to improve the accuracy of future estimates, especially for analogous and parametric estimating.
- When using expert judgment, employ techniques to reach a consensus among multiple experts and reduce individual bias.
5. Account for Risk and Uncertainty
Accounting for risk and uncertainty aids your agency in preparing for potential issues that could impact project costs as well as provide a buffer for unforeseen circumstances.
Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential cost impacts. Use techniques like sensitivity analysis or Monte Carlo simulation to quantify the effect of risks on your estimates. Include appropriate contingency reserves in your budget.
Tips to consider:
- Develop a comprehensive risk register that includes potential cost impacts for each identified risk, and update it regularly throughout the project.
- Use a tiered contingency approach, allocating different levels of reserves for known risks and unknown uncertainties.
6. Compile and Review the Cost Estimate
Compiling as well as reviewing the cost estimate ensures that all components are accounted for and the overall estimate is reasonable. The step helps identify any inconsistencies or areas that may need further refinement.
Aggregate all cost components into a comprehensive estimate. Review the estimate for completeness, accuracy, and reasonableness. Conduct a peer review or engage external experts to validate your estimates.
Tips to consider:
- Use a structured checklist to ensure all cost elements are included and no aspects of the project have been overlooked in the estimation process.
- Conduct a formal review meeting with key stakeholders to present and discuss the estimate, gathering feedback as well as buy-in.
7. Document and Communicate the Estimate
Thorough documentation and clear communication of the cost estimate are essential for stakeholder understanding as well as project approval. Creating a clear project management communication plan ensures all stakeholders receive the cost estimate accurately and on time. It provides a baseline for future cost control and helps manage expectations.
Create a detailed cost estimation report that outlines all assumptions, methodologies, and calculations. Present the findings to stakeholders, clearly explaining the rationale behind the estimates and any areas of uncertainty.
Tips to consider:
- Develop a standardized cost estimation report template that includes sections for methodology, assumptions, detailed breakdowns, and sensitivity analysis.
- Establish a clear process for updating and re-baselining estimates as the project progresses as well as its detailed information becomes available.
How to Utilize Agency Management Software for Project Cost Estimation?
Kooper is an all-in-one agency management software that offers a comprehensive solution for project cost estimation, budgeting, and lifecycle management. Its integrated approach provides several key benefits for agencies, professional services businesses, and consultancies.
Here is how Kooper can be used for project costing and resource management,
1. Time Tracking and Resource Management
Kooper offers detailed time tracking capabilities, allowing agencies to accurately measure the time spent on various project tasks. The data is significant for refining future cost estimates and understanding resource utilization. The resource management feature helps in allocating team members efficiently, ensuring optimal use of skills and avoiding overallocation.
2. Project Budgeting and Financial Planning
The software provides robust budgeting tools that allow agencies to create detailed project budgets. Teams can improve project cost estimation by creating a practical project budget plan before execution. It enables real-time tracking of actual costs against estimated costs, giving project managers immediate visibility into budget variances. The tool helps in the early identification of potential overruns and allows for timely corrective actions.
3. Profitability Tracking
Kooper calculates project profitability in real-time, considering all costs including time spent, expenses, and overheads. It is invaluable for agencies to ensure each project contributes positively to the bottom line and helps in making data-driven decisions about resource allocation as well as pricing strategies.
4. Forecasting and Capacity Planning
The platform offers forecasting tools that help agencies predict future resource needs and potential revenue. It assists in long-term planning and helps balance workloads across the team. The capacity planning feature ensures that the agency doesn’t overcommit or underutilize its resources.
5. Invoicing and Expense Tracking
Integrated invoicing features streamline the billing process, reducing administrative overhead. The expense tracking functionality ensures all project-related expenses are captured and billed appropriately, improving overall project profitability.
6. Customizable Dashboards and Reporting
Kooper provides customizable dashboards and detailed reporting features. These allow agency leaders to get a bird’s-eye view of all projects, track key performance indicators, and make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Best Practices for Cost Estimation in Project Management
Mastering cost estimation is key to project success as well as the agency’s growth. Here’s how to avoid surprises and ensure smooth project management.
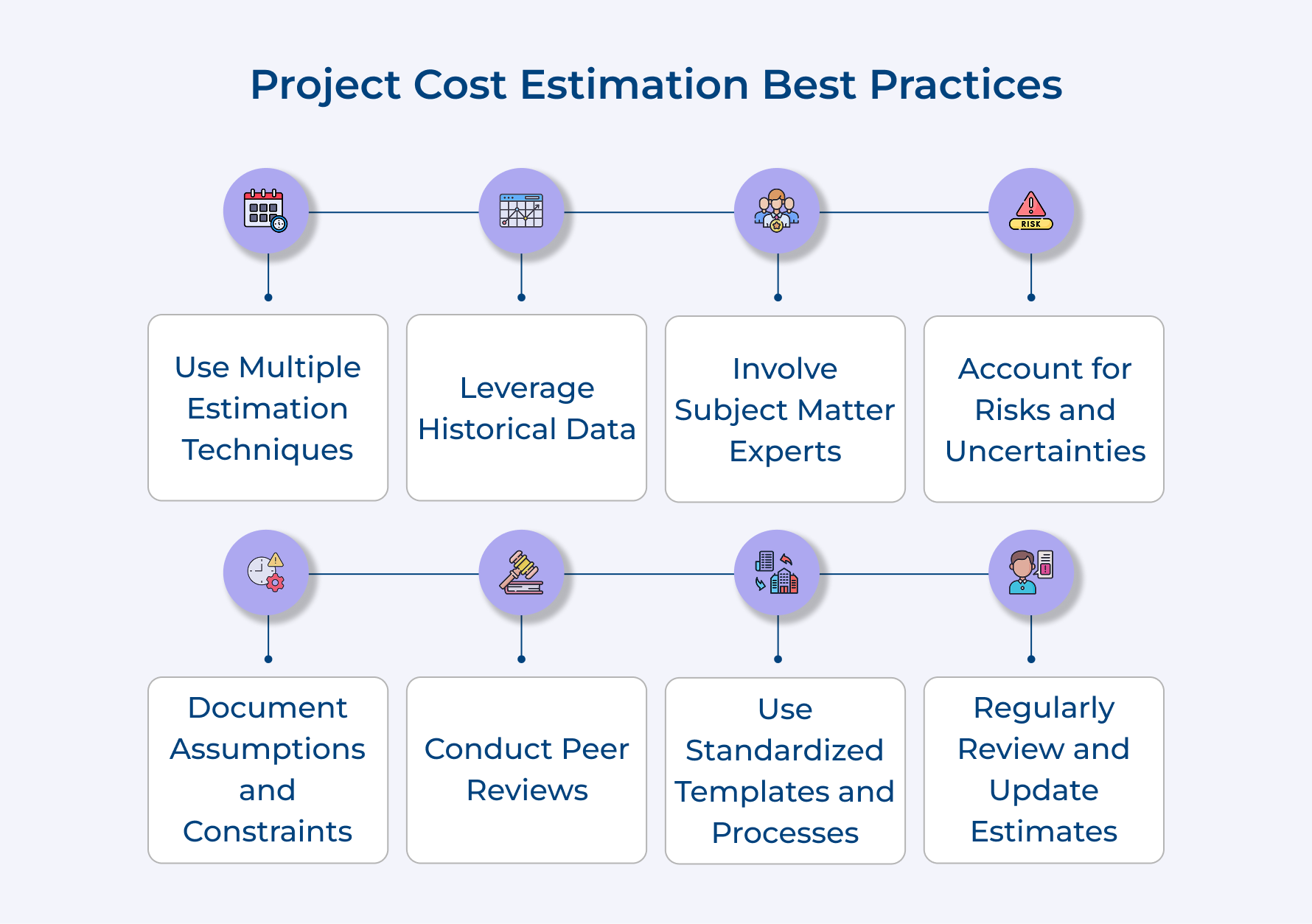
1. Use Multiple Estimation Techniques
Don’t rely on a single method. Combine techniques like analogous estimating, parametric estimating, and bottom-up estimating. The multi-faceted approach provides a more comprehensive and accurate cost picture, balancing the strengths as well as weaknesses of each method.
2. Leverage Historical Data
Maintain a database of past project costs and use the information to inform current estimates. Analyze trends, identify cost drivers, and use this data to improve the accuracy of future estimates. Regularly update the database to ensure its relevance.
3. Involve Subject Matter Experts
Engage team members and subject matter experts in the estimation process. Their hands-on experience along with technical knowledge provides helpful insights into potential costs and risks that might not be apparent from historical data alone.
4. Account for Risks and Uncertainties
Incorporate risk assessment into your cost estimation process. Use techniques like Monte Carlo simulation to model the potential impact of risks on project costs. Include appropriate contingency reserves based on the project’s risk profile.
5. Document Assumptions and Constraints
Document all assumptions and constraints used in developing the cost estimate. The transparency helps stakeholders understand the basis of the estimate and provides crucial context for future review or adjustment.
6. Conduct Peer Reviews
Implement a peer review process for cost estimates. Having another experienced project manager or cost estimator review your work can help identify oversights, validate assumptions, and improve overall estimate accuracy.
7. Use Standardized Templates and Processes
Develop standardized templates and processes for cost estimation. It helps maintain consistency across projects and makes it easier to compare estimates, while also helping less experienced team members produce more reliable estimates.
8. Regularly Review and Update Estimates
Treat cost estimation as an ongoing process. Regularly review and update estimates as the project progresses as well as more information becomes available. Implement a formal change control process to manage updates to the cost baseline.
Strengthening Profitability with Smart Project Cost Estimation
Project cost estimation is a critical process that determines the financial resources required for successful project completion. An accurate estimate helps in budgeting, resource allocation, and financial planning, ensuring projects stay within their allocated budgets. The process involves analyzing various factors, including materials, overhead and potential risks.
Effective cost estimation relies on various techniques, such as expert judgment, analogous estimating, and parametric modeling. Nevertheless, precise cost estimation enhances decision-making leading to improved project outcomes and reduced financial risks. Implementing robust estimation practices builds accountability and supports effective project management.
Limit time — not creativity
Everything you need for customer support, marketing & sales.
Ronak Shah is part of the marketing team at Kooper, where he specializes in crafting strategic content that supports business growth and brand visibility. With a strong interest in digital marketing, performance strategy, and customer engagement, he turns complex ideas into clear, actionable insights for agencies and growing businesses.