A Complete Guide to Cost Baseline in Project Management
- What is a Cost Baseline in Project Management?
- Why are Cost Baselines Important?
- How to Create a Cost Baseline in Project Management?
- Types of Baseline in Project Management
- Difference Between Project Budget and Project Cost Baseline
- Future-Proofing Projects with a Strong Cost Baseline
- FAQs about Cost Baseline in Project Management

Key Highlights:
- Cost baseline in project management helps allocate resources strategically with time-phased, contingency-inclusive financial planning.
- Simplify reporting for stakeholders with real-time financial performance insights.
- Monitor costs against planned budgets to prevent overruns and stay on track.
When managing projects, have you ever wondered how to keep costs in check without constantly crunching numbers? That’s where the concept of a cost baseline comes into play.
It is nothing less than being the financial backbone of your project—guiding your spending, tracking your progress, and helping you avoid budget overruns.
A cost baseline in project management isn’t just a fancy term; it’s a practical tool that sets clear expectations for everyone involved.
Let’s break down the essentials of creating and managing a cost baseline, so you can take charge of your project’s financial health
What is a Cost Baseline in Project Management?
A cost baseline is a formally approved, time-phased budget that serves as a reference point for measuring and monitoring a project’s financial performance. It represents the authorized cost estimates for the entire project broken down into specific periods, typically including contingency reserves but excluding management reserves.
The baseline in project management becomes the foundation against which all actual costs are compared throughout the project lifecycle. Providing a clear picture of expected costs over time, helps stakeholders understand the project’s financial requirements and supports effective resource allocation.
Key objectives:
- Budget control: Establishing a project cost baseline allows for effective monitoring of expenditures, ensuring that the project stays within its financial limits.
- Performance measurement: It serves as a benchmark against which actual costs can be compared, helping assess project performance and identify any discrepancies.
- Variance analysis: The cost baseline facilitates variance analysis, enabling project managers to investigate the reasons behind cost overruns or underruns and implement necessary adjustments.
- Stakeholder communication: Having a clear cost baseline improves communication with stakeholders, providing them with transparency regarding the financial status of the project.
Why are Cost Baselines Important?
Ever felt like your project budget has a mind of its own? A cost baseline purpose acts as your roadmap, keeping your spending aligned with your goals and ensuring you stay on track.
Performance tracking and control: A cost baseline helps you track actual expenses against your planned costs, so you can quickly spot any variances and take action before small issues snowball into big financial headaches.
Transparency in financial reporting: Cost baselines simplify financial reporting by giving stakeholders a clear view of the project’s financial health—what’s been spent, what’s left, and how the budget is shaping up.
Ensures realistic budget allocation: Breaking down costs by project phases and activities ensures your budget isn’t just wishful thinking. It lets you allocate funds strategically, ensuring resources align with project requirements and timelines.
Establishes clear financial responsibilities: Cost baselines bring clarity to the table. They define who’s responsible for managing expenses, tracking costs, and making budget-related decisions, ensuring everyone’s on the same page.
Improved forecasting: With a robust cost baseline, you can predict potential overruns early and make accurate predictions about the final project costs.
Project success measurement: Finally, cost baselines are key to evaluating project success. They help you determine if your financial performance aligns with your goals and whether you’ve delivered on your objectives within the approved budget.
How to Create a Cost Baseline in Project Management?
Creating a cost baseline can be cumbersome for a few managers if not many. Here’s the step-by-step list to help make an efficient list that ensures a smoother workflow.
1. Collect and Organize Project Cost Information
Creating a solid cost baseline starts with one key ingredient: organized cost information.
When you have a clear picture of all project expenses, it’s much easier to avoid missing critical costs and plan your finances with confidence.
Comprehensive data collection is the backbone of accurate budgeting and ensures every decision you make is backed by solid numbers.
Project managers use this organized data to craft detailed budget estimates, design cost breakdown structures, and identify spending patterns.
The structured approach doesn’t just help allocate funds effectively across project phases—it also highlights areas where you can optimize costs.
2. Identify Costs
Cost identification is crucial for defining the components of project cost baseline. Categorizing expenses into direct, indirect, fixed, and variable costs helps in realistic resource allocation.
Here’s why it matters,
- No budget surprises: Identifying all expenses upfront ensures nothing catches you off guard down the line.
- Accurate resource allocation: With a clear view of costs, you can allocate resources effectively without over- or underestimating.
- Realistic project planning: A thorough cost breakdown supports better planning and keeps financial transparency intact.
How can teams approach cost identification?
- Categorize expenses into direct, indirect, fixed, and variable costs.
- Build a detailed cost breakdown structure to make budget allocation easier.
- Use this structure to track spending and find areas for potential cost optimization.
3. Establish Time-phased Budget
Time-phasing allows for the realistic distribution of costs across the project timeline, helping in how to calculate cost baseline in project management by aligning expenses with milestones and cash flow needs.
It helps in cash flow management, and resource allocation planning, as well as provides a framework for tracking expenditures against planned spending at specific points in time.
Project managers can align costs with project activities and milestones, creating a timeline-based spending plan. Hence, this alignment enables better resource management and helps in identifying periods of high financial activity.
How to leverage it better?
- Create detailed cost-loading schedules that align with project milestones and deliverables
- Use S-curves to visualize and validate the reasonableness of cost distribution over time
- Incorporate seasonal variations and market fluctuations in cost estimates for different periods
4. Include Contingency Reserves
Allocating contingency reserves helps safeguard against unforeseen costs. Teams can use cost baseline formula methods such as quantitative risk analysis to determine necessary reserves.
Teams can allocate specific amounts or percentages as reserves based on risk assessment.
These reserves can be distributed across different project phases or held centrally for overall project risk management.
Calculate contingency reserves using quantitative risk analysis methods for more accurate estimations. Document clear guidelines for accessing and using contingency funds, including approval processes.
5. Review and Validate Estimates
Cost validation is like a reality check for your project budget. It ensures your estimates are accurate, realistic, and based on solid assumptions. This is one of the cost baseline best practices to maintain financial credibility.
By validating your costs, you can catch errors or oversights early, saving you headaches later. Plus, it boosts stakeholder confidence in your cost baseline—always a win!
How to validate your costs effectively?
- Conduct peer reviews and expert assessments to spot any inaccuracies.
- Use comparative analyses to benchmark your estimates against similar projects.
- Try multiple estimation techniques to cross-check figures and ensure your projections are solid.
6. Obtain Formal Approval
The importance of cost baseline is emphasized when obtaining stakeholder approval, as it ensures accountability and alignment across teams.
Formal approval ensures everyone on the team and among stakeholders is on the same page about the budget as well as their roles in sticking to it.
By documenting the approval, you’re holding everyone accountable to the financial framework you’ve agreed on.
Handle the approval process by,
- Setting up approval workflows that involve all the key decision-makers.
- Keeping records of the approvals, along with any conditions or constraints tied to them.
- Preparing thorough baseline documentation, including all the data and assumptions behind the numbers.
- Scheduling formal review meetings with stakeholders to address concerns before getting the final green light.
- Having clear escalation paths in place to handle any approval issues quickly and efficiently.
Formal approval isn’t just a formality—it’s essential for ensuring smooth project execution and financial accountability.
7. Set Up Monitoring Systems
Monitoring systems enable tracking of actual costs against the baseline. They provide early warning of potential cost overruns and support timely decision-making for cost control measures.
Implement earned value management systems and regular reporting mechanisms. Use monitoring data to analyze trends, identify variances, and make informed decisions about cost management.
8. Document Control Procedures
Control procedures ensure consistent management of cost-related changes. They maintain baseline integrity while providing a structured approach to handling necessary modifications throughout the project.
Develop as well as implement change control processes that govern how cost changes are requested, evaluated, and approved.
Maintain detailed records of all baseline modifications and their justifications. Establish a change control board with clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
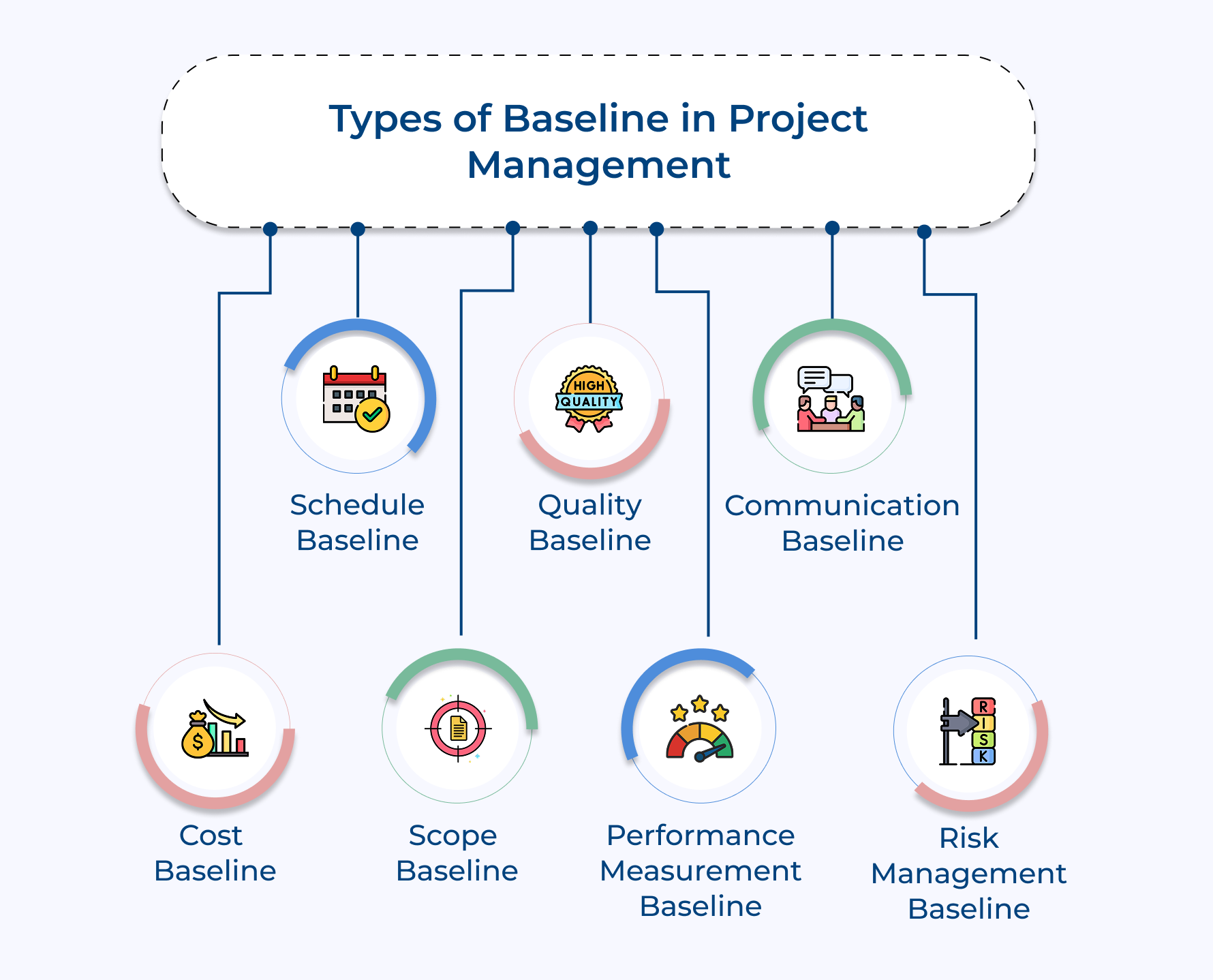
Types of Baseline in Project Management
Cost isn’t the only baseline that the project manager considers. There are multiple aspects too. Let’s explore some of the crucial baseline involved in project management.
1. Cost Baseline
The cost baseline is the approved version of the project budget, consisting of all estimated costs associated with the project. It serves as a reference point for monitoring expenditures and managing financial performance throughout the project lifecycle.
Essential Elements:
- Estimated costs: Detailed breakdown of expected expenses.
- Contingency reserves: Funds allocated for unforeseen costs.
- Budget periods: Timeline for when costs will be incurred.
- Cost management plan: Guidelines for monitoring and controlling costs.
2. Schedule Baseline
The schedule baseline outlines the approved project timeline, detailing the planned start and finish dates for all activities. It’s a reference for tracking progress and assessing delays or changes during the project.
Key Components:
- Planned activities: List of all tasks and milestones.
- Start and finish dates: Specific timelines for each activity.
- Dependencies: Relationships between tasks.
- Critical path: Sequence of tasks determining project duration.
3. Scope Baseline
When it comes to scope baseline, it defines the approved project scope, including deliverables and boundaries. It helps prevent scope creep by ensuring that any changes to the project scope are managed effectively.
Crucial Factors:
- Project scope statement: Description of objectives and deliverables.
- Work breakdown structure (WBS): Hierarchical breakdown of project tasks.
- WBS dictionary: Detailed descriptions of WBS components.
4. Performance Measurement Baseline
Performance measurement baseline integrates cost, schedule, and scope baselines to assess overall project performance. It allows project managers to analyze variances and track project health effectively.
Significant Aspects:
- Integrated baseline: Combination of cost, schedule, and scope baselines.
- Performance metrics: Key indicators like Earned Value (EV).
- Variance analysis: Tools for identifying discrepancies between planned and actual performance.
5. Quality Baseline
The quality baseline establishes the quality standards and metrics for project deliverables. It ensures that the project meets predefined quality criteria throughout its execution.
Key Components:
- Quality standards: Criteria that deliverables must meet.
- Quality metrics: Specific measurements for evaluating quality.
- Quality assurance plan: Guidelines for ensuring adherence to quality standards.
6. Communication Baseline
The communication baseline outlines how information will be shared among stakeholders. It ensures that everyone is informed about project status, changes, and key decisions.
Principal elements:
- Communication plan: Document detailing methods and frequency of information sharing.
- Stakeholder engagement: Identification of stakeholder communication needs.
- Reporting templates: Standard formats for progress reports and updates.
7. Risk Management Baseline
The risk management baseline identifies potential risks and outlines strategies for mitigating them. It helps project managers proactively address risks throughout the project lifecycle.
Main Components:
- Risk register: Comprehensive list of identified risks and their attributes.
- Risk response plan: Specific actions to mitigate or respond to risks.
- Risk analysis techniques: Methods for evaluating risk impact and probability.
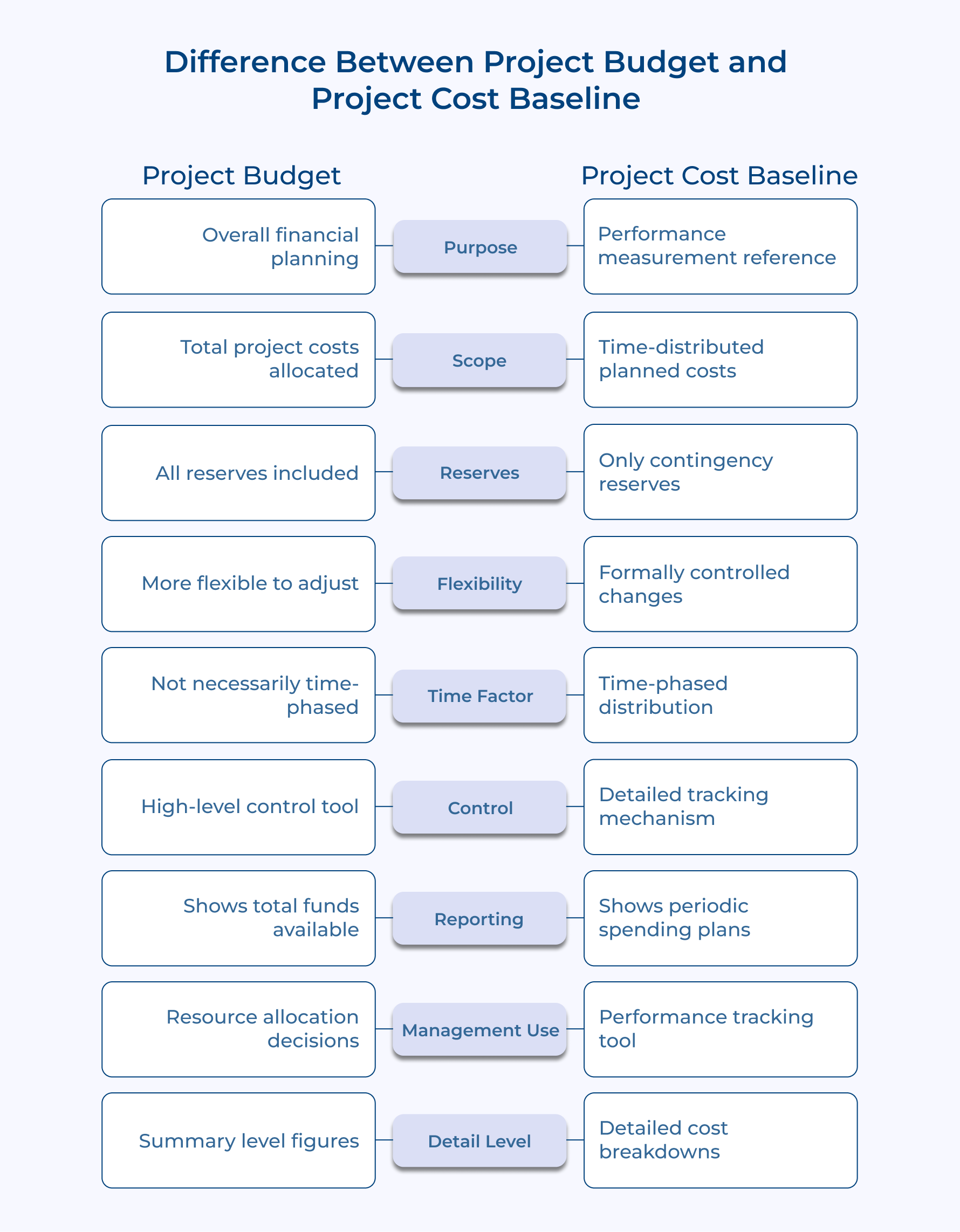
Difference Between Project Budget and Project Cost Baseline
Ever wondered what sets a project budget apart from a project cost baseline? While they might sound similar, these two play distinct roles in keeping your project finances on track.
1. Composition and Structure
The project budget covers planned expenses and includes a safety cushion (management reserves) for unexpected risks or opportunities. It’s the total financial pie you can work with.
The cost baseline is a more detailed breakdown of approved costs spread over time. It doesn’t include management reserves but does factor in contingency reserves for known risks.
2. Purpose and Usage
As a planning tool, a project budget helps with making big decisions, allocating resources, and ensuring the funds are there when you need them. Plus, it has room for strategic tweaks along the way.
The cost baseline is more like a fine-tuned performance tracker. It’s all about measuring how your spending stacks up against your plan, helping with earned value calculations, and spotting variances over time.
3. Flexibility and Changes
Flexibility is the synonym for project budget. It can shift with changes in strategy or market conditions without too much hassle. You can adjust it without jumping through too many hoops.
However, the cost baseline is more rigid. Any changes require formal approval and detailed documentation to keep performance measurements accurate as well as consistent.
4. Timing and Distribution
The project budget isn’t tied to specific timeframes. It’s more about the overall allocation. The project budget might follow broader accounting periods or fiscal year timelines.
The cost baseline is time-phased, meaning it shows exactly when you plan to spend money throughout the project. It’s all about precision in timing.
5. Reserve Handling
The project budget includes contingency reserves for known risks and management reserves for the unexpected. It’s your all-encompassing financial safety net.
To be more specific, the cost baseline only includes contingency reserves for identified risks, leaving out management reserves for a more focused tracking approach.
6. Management Perspective
The project budget is aligned with the big-picture view, supporting organizational and portfolio-level decisions. It helps with strategic planning and distributing resources across projects.
The cost baseline is zoomed in on project-level details. It’s a hands-on tool for managing day-to-day activities and making tactical decisions.
Future-Proofing Projects with a Strong Cost Baseline
The cost baseline plays a vital role in project management by providing a structured framework for budgeting and financial oversight. Establishing an approved reference point allows project managers to measure actual costs against planned expenditures, facilitating the identification of variances and timely corrective actions.
The impact of a well-defined cost baseline is significant, enhancing accountability, optimizing resource allocation, and reducing the likelihood of cost overruns. Such benefits contribute to a more efficient project management process, enabling teams to focus on delivering value.
Implementing a robust cost baseline ensures effective project delivery while building stakeholder confidence. It leads to projects completed on time and within budget, highlighting the importance of sound financial planning in achieving project success.
Limit time — not creativity
Everything you need for customer support, marketing & sales.
Neeti Singh is a passionate content writer at Kooper, where he transforms complex concepts into clear, engaging and actionable content. With a keen eye for detail and a love for technology, Tushar Joshi crafts blog posts, guides and articles that help readers navigate the fast-evolving world of software solutions.